Protecting sensitive business data has become increasingly important in today’s socially-distanced, remote-working world. This is especially true for securities and investments companies that collect and manage an enormous amount of personal data of their customers.

Taking into account the rising cybersecurity threats, India’s markets regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has formulated a comprehensive cybersecurity policy framework titled "Cyber Security and Cyber Resilience Framework for Stock Brokers/Depository Participants" and "Mutual Funds/Asset Management Companies (AMCs)."
Through these two policy frameworks, SEBI has issued clear data protection regulations that Indian Stock Brokers, Depository Participants, Mutual Fund Companies and AMCs should follow. Below are the five key points outlined in these two regulations:
1. Sensitive data, whether in-motion or at-rest, should be identified and encrypted using strong encryption methods like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA), etc.
2. Data masking should be adopted wherever possible.
3. Specific personnel should be identified to take charge of the encryption methodologies and storage of encryption keys so that they don’t fall into the wrong hands.
4. When a company application transmits sensitive data via the Internet, it should be over a secure, encrypted channel to prevent Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attacks. Strong transport encryption mechanisms like Transport Layer Security (TLS), also known as Secure Socket Layer or SSL should be used.
5. Passwords, security PINs, etc. should never be stored in plain text. Instead, they should be one-way hashed using strong cryptographic hash functions before storage. Additionally, one-way cryptographic hashes should be used to ensure that the stored password hashes are never transformed into their original plaintext values.
Just like SEBI’s regulations, the practice of data encryption and key management is recommended by almost all data protection regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). In India, regulators like the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and Reserve Bank of India (RBI) have time and again issued circulars mandating the adoption of data encryption and key management. Furthermore, the upcoming Personal Data Protection Act in India also regulates data encryption and key management for protecting sensitive data. In 2018, we comprehensively covered the Personal Data Protection Act in a three-part blog post series (Part 1, Part 2 and Part 3).
Failure to comply with data protection regulations can cause significant damages in penalties as recently experienced by SPARTOO, a European online footwear retailer, who received a fine of €250,000 by French data protection authority CNIL for violating multiple articles of GDPR.
Taking a cue from GDPR, the upcoming Personal Data Protection Act in India prescribes a stiff penalty of 4% of a company’s global turnover or Rs. 15 crores; whichever is higher, for non-compliance to the mandated data protection guidelines.
Complying With Various Data Protection Regulations In India
Based on specific data protection regulations, securities and investments companies should invest in certain technologies in order to avoid steep fines and penalties. These solutions include:
1. Data Encryption
With a proliferation of disparate applications spread across on-premises, cloud and virtual environments, encrypting sensitive data wherever it resides becomes paramount to enterprise-wide data protection.
Thales’s vast range of data encryption solutions not only helps organisations breach-proof their sensitive data but also helps them cohesively meet compliance regulations across multiple data protection regulations.
2. Key Management
Since encryption keys evolve through multiple phases during their lifetime – like generation, registration, distribution, rotation, archival, backup, revocation and destruction, securely and efficiently managing these keys at each phase of their lifecycle becomes fundamental to protection of data.
Furthermore, to ensure that the encryption keys don’t fall in the wrong hands, and thereby render the entire encryption exercise futile, encryption keys should be decoupled i.e. separated, from encrypted data.
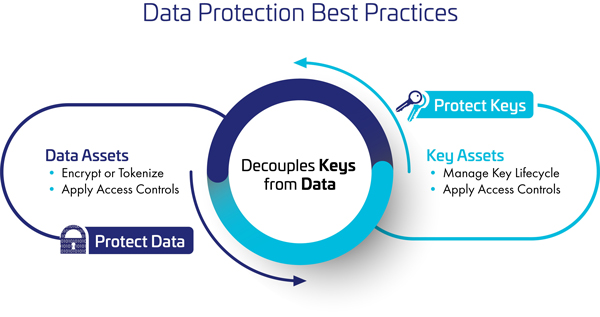
Thales’s CipherTrust Manager is a strong enterprise key management solution that helps organisations centrally manage their encryption keys from varied encryption systems, provide granular access control and configure security policies. This not only simplifies multiple administrative challenges associated with managing encryption keys, but also ensures that all the keys are secure and provisioned to authorised encryption systems.
To Sum It Up
With cyberattacks increasing in India by as much as 500% since the COVID-19 lockdown was imposed in March this year (as estimated by Mr. Pavan Duggal, a Supreme Court advocate and cyber law expert), protecting sensitive business data has become more important than ever before.
New insights from the 2020 Thales Asia-Pacific Data Threat Report reveal that nearly half (45%) of Asia-Pacific (APAC) organisations suffered a breach or failed a compliance audit in the last year.
Encrypting sensitive data and securely managing the encryption keys centrally not only mitigates data breach risks but also helps organisations adhere to data protection regulations.
Securing an organisation’s most sensitive data no longer has to be complex. Find out how Thales’s new CipherTrust Data Security Platform can simplify data security.

 Ashesh Thanawala | Sales Director – India & SAARC
Ashesh Thanawala | Sales Director – India & SAARC