Thales Blockchain Solutions
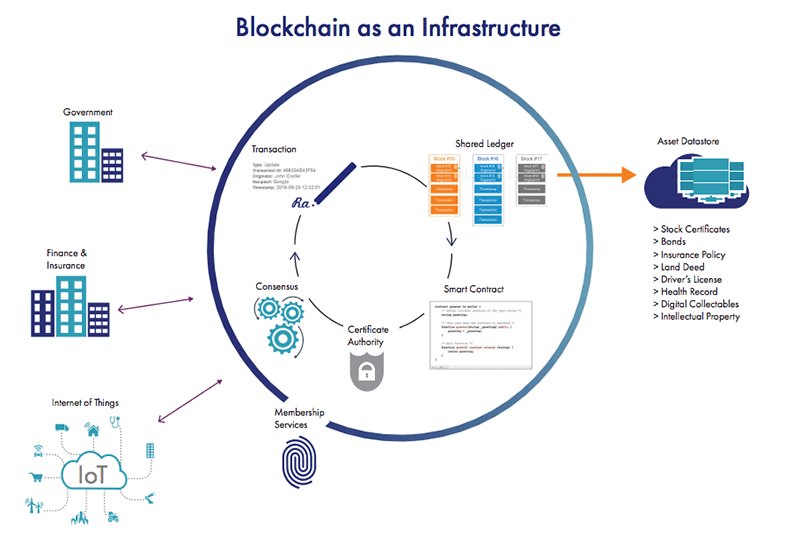
Although blockchain is based on sophisticated math and is secure at its foundation with its decentralized approach, there are ways to fool the blockchain to gain advantage. Ensure you build security into your solution from the ground up, always storing your keys in a hardware-based solution to avoid those pitfalls and remain protected.
Luna Network HSMs are designed to store the private keys used by blockchain members to sign all transactions in a FIPS 140-2 Level 3 dedicated cryptographic processor. Keys are stored throughout their lifecycle; ensuring cryptographic keys cannot be accessed, modified or used by unauthorized devices or people. Cryptographic keys kept in software are at risk of theft, compromising the entire blockchain ledger.
ProtectServer HSMs, like the Luna Network HSMs, are designed to protect cryptographic keys against compromise while providing encryption, signing, and authentication services.
Both Luna and Protect Server HSMs extend native HSM functionality by enabling the development and deployment of custom code within the secure confines of the FIPS 140-2 Level 3 validated Thales HSM as a part of the firmware. Functionality Modules (FMs) allow you to customize your Thales HSM’s functionality to suit the needs of your organization, including the implementation of Quantum algorithms.
Luna Cloud HSM Services. In addition to our on-premises HSM solutions, Thales also offers a Luna Cloud HSM solution through Data Protection On Demand (DPoD). DPoD offers an as a service billing model with no hardware to deploy and maintain.
SafeNet Authentication Service (SAS) will substantially reduce your total cost of operation and tailor authentication to meet your unique needs with this fully automated, highly secure authentication-as-a service with flexible token options.