Cybercriminals have been making a run on your data with ransomware attacks over the last decade in increasing frequency. They wreak havoc by bringing critical infrastructures, supply chains, hospitals, and city services to a grinding halt. Cybersecurity Ventures predicts by 2031 ransomware will cost victims $265 billion annually, and it will affect a business, consumer, or device every 2 seconds.
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware is a vicious type of malware that infects your laptop/desktop or server. Cybercriminals use it as a launching pad to block access to business-critical systems by encrypting data in files, databases, or entire computer systems, until the victim pays a ransom. It is a form of cyber extortion. Cybercriminals hold your data hostage by encrypting it, and threaten to destroy it or publish it, unless a large ransom is paid.
Common Infection Vectors
The most common vectors of infecting victims with ransomware are the following.
- Phishing Emails: Cybercriminals send an email containing a malicious file or link, which deploys malware when the recipient unknowingly clicks opens the file attachment or clicks on the link. This results in the malware (binary) to run as a process on the victim’s end user system (endpoint) or server.
- Exploit Software Vulnerabilities: Cybercriminals can take advantage of security weaknesses in widely used software to gain access to a victim’s system and deploy ransomware. Wannacry is one of the most famous ransomware that targeted a vulnerability in Microsoft Windows Servers.
- Remote Desktop Vulnerabilities: Cybercriminals can gain administrative access to an endpoint/server using a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) service, using a brute-force method trying to guess passwords, or by using stolen credentials purchased on the Dark Web.
Baseline security practices using perimeter controls such as next generation firewalls, secure email/web gateways and focusing on closing vulnerability gaps alone have not been sufficient to prevent ransomware attacks. The main challenge facing Fortune 500 companies is to safeguard business critical data from being encrypted by unauthorized processes and users on endpoints and servers.
Introducing Thales’ Ransomware Protection
Thales’ CipherTrust Transparent Encryption – Ransomware Protection (CTE-RWP) provides early detection of rogue processes and a non-intrusive way of protecting files/folders from ransomware attacks with minimal configuration.
Early Detection
CTE-RWP watches for abnormal I/O activity on volumes hosting business critical data on a per process basis. It uses process-based models to dynamically detect suspicious file I/O activity. It gives administrators a choice of alerting and/or blocking file access before ransomware can take hold of your endpoints/servers.
Transparent Data Protection
CTE-RWP requires minimal configuration – identifying volumes that hold business-critical data as “guard points”. It continuously monitors for abnormal file I/O activity caused by ransomware infected processes.
Easy Deployment
CTE-RWP enables administrators to start with ransomware protection alone, without setting up restrictive access control and encryption policies on a per file/folder basis, which is available in a CTE license.
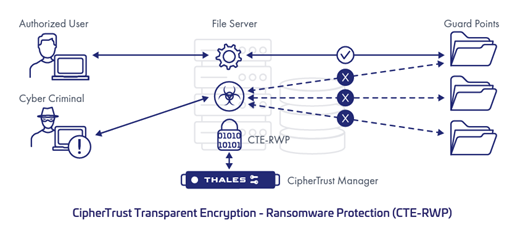
Enhanced Paths for Complete Data Protection
Customers of Thales’ Ransomware Protection (CTE-RWP) can maximize ransomware protection on their endpoints/servers, by licensing CipherTrust Transparent Encryption (CTE) in addition to CTE-RWP.
Add Fine-grained Access Control
CTE enables administrators to add the following robust access control and encryption techniques for rogue ransomware binaries to corrupt business critical data.
- Fine-grained access control:
- Administrators can define who has access to read/write and encrypt/decrypt files in folders that are protected.
- A “trusted” list of files (binaries) can be specified designating approved access to protected folders (Guard-Points) where business critical data resides.
- Data at rest encryption: Encrypt business critical data, wherever it resides, on servers on-premises or in the cloud. It makes data worthless to intruders since they cannot monetize encrypted data by threatening to publish it.
Add Multi-factor Authentication
Customers can add Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) for CipherTrust Encryption (CTE), to get an additional layer of protection at the folder/file level. MFA for CTE prompts system administrators and privileged users to demonstrate an additional factor of authentication beyond passwords when they try to access to sensitive data sitting behind Guard-Points.
MFA for CTE is available for the Windows platform. It supports integrations with multiple authentication providers including Thales’ SafeNet Trusted Access, Okta and Keycloak.
Stop Ransomware Attacks in their Tracks with Thales Solutions
To effectively block ransomware from taking your data hostage, you need a strong data security solution. The CipherTrust Data Security Platform offers multiple data security solutions, that help your discover, protect and monitor business-critical data. CipherTrust Transparent Encryption Ransomware Protection solution provides a great start for businesses to implement a robust ransomware detection and protection strategy.

 Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing