Technology innovation creates business value for organizations, but also new challenges for data privacy and protection. The pandemic has revealed the importance of technology to enable us to work from home to provide business continuity and to keep in contact with our extended family and friends.
However, in some cases, a serious downside occurs when privacy has been sacrificed to fast track the digital transformation. These digital transformations are vital for business to continue, but also introduces new risks. A research report issued by International Association of Privacy Professionals titled “Privacy in the wake of COVID-19” shows that 60 percent of those who adopted new technologies for working from home either skipped or expedited security/privacy reviews, creating a completely new set of risks for companies. Probably also increasing the cost of any resultant data breach, as mentioned in the 2020 IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report.
The good news is that managing privacy does not have to be yet another daunting task on top of the already herculean feat of implementing digital transformation for business continuity. To help organizations better plan their privacy and security strategies, we need to recognize the challenges that business leaders have to address to achieve a holistic data privacy and protection implementation.
New regulation, new challenges
There’s been growing regulatory pressure on both sides of the Atlantic. The GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in the United States, contain stringent protocols for the management of user data and both threaten steep fines for businesses that get it wrong. According to PwC’s Risk Atlas, we have over 1,800 data privacy regulations around the world - in regions including North America, Latin America, Asia, Europe and Oceania. The landscape is rapidly evolving, with more countries joining the cause on a regular basis.
The fallout from data privacy violations can cripple any organization for a long time. From devastating financial losses due to heavy fines, penalties and litigation costs, and lost customer business and credibility to reputational damage. Small businesses, with much lower resources, are likely to be hit even harder. Many of them may go bankrupt or out of business. Most of the organizations will likely face delays in their sales cycles due to customer concern over data privacy.
An increasing number of privacy and security solutions aim to support organizations facing this kind of pain. Having a partial understanding of your data or operating over a reduced area of the problem is like leaving the backdoor open. Indeed, the “Market Guide for File Analysis Software” report issued by Gartner reveals that through 2024, 80% of information governance programs that do not include unstructured, semi-structured and structured data within the same governance program will fail, up from 30% today.
Stepping Stones to a Secure Organization
Data privacy is a step in the right direction for a holistic data security and privacy strategy. Organizations need to establish a privacy first strategy to make it a competitive business advantage. Organizations that are using data science to boost their business will have to comply with multiple regulations. In addition, 71% of consumers claim that they will not conduct business with companies that give away sensitive data without permission, as highlighted in the 2020 McKinsey Research Report. This leaves corporations struggling to cope with growing state, global and industry-specific laws and market demands, creating significant risks for them.
To protect information, the target of most attacks, you need to know which data is critical, where it resides, how it is used and who has access to it. There is a need to define the policies to ensure that consumers’ Personally Identifiable Information (PII) is collected, shared and processed in an appropriate and compliant manner.
Organizations need to move towards a more holistic and proactive approach to addressing security threats and managing compliance requirements in today’s data-driven economy. Thus, today, more than ever, enterprises need strong IT governance based on sound risk management in order to restore confidence in the security and privacy protections provided by governments and industries worldwide.
Better data visibility to the rescue
Having visibility into organization’s sensitive data and defining what data is sensitive, and how sensitive, is a critical first step in any holistic data security and privacy program. Organizations can’t protect something they don’t know exists! As mentioned in the Forrester Report “Shift From Privacy Readiness to Sustained Compliance” organizations have to prioritize data discovery and classification. Forrester makes a strong argument for building a repeatable process for defining, analyzing, and defending data as it not only supports compliance with relevant industry-specific regulatory mandates but also provides security and IT teams with full visibility into how the data is being accessed, used, and moved around the organization.
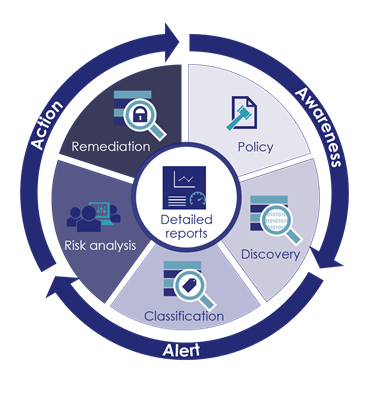
5 Steps to Effective Data Privacy and for a Secure Organization
There are five steps to effective data privacy:
1. Set policies to search for sensitive data in different data stores
Determining what types of sensitive data exist within your organization can present challenges. It is an effort that should be organized around business processes and driven by process owners.
2. Discover the location of your data
Data discovery tools can help generate an inventory of structured and unstructured data and help you understand exactly where your company’s data is stored, regardless of the format or location. These tools also help address difficulties around identifying data owners by providing insights about users who are handling data in the cloud or on-premises.
3. Identify and classify data
Only after you know where your data is stored can you identify and then classify it so that it’s appropriately protected. Having visibility into the category of the data the organization holds, provides an understanding of the data to protect, how to do it and how to use the different data types.
4. Complete a risk assessment of sensitive data
Identify the risks associated with the personal and sensitive data based on sensitivity levels or data types. By risk, we mean likelihood of that data being exposed, as well as risk scores that can rank the data at most risk. The risk should consider different aspects such as number of occurrences, type of data, location, among others. This understanding of the risk allows prioritization of the remediation actions.
5. Remediate data at risk
Once organizations have a clear understanding of their personal and sensitive data and its risks, they can now tie them back to the privacy obligations and determine the most appropriate measures to minimize risks and comply with the privacy goals.
Again, ideally speaking, organizations should try to automate remediation using smart policies. For example, if an organization finds PCI data in a public database, it can have a policy to tokenize that specific data automatically. By contrast, if they have PII in a public file share, they might want to have a policy to encrypt automatically the file share in question. Integrated and automated solutions help eliminate blind spots and human error, which can make a huge difference in complying with varied regulations.
How Thales can help
Thales CipherTrust Data Discovery and Classification provides a single pane of glass to help organizations efficiently locate sensitive data, both structured as well as unstructured, across a wide range of locations such as cloud, data lakes and many more. With a streamlined process and rich visualizations, it offers a clear view of the sensitive data and risks so that companies can take appropriate steps to protect what matters the most to them.
This solution is part of the CipherTrust Data Security Platform from Thales, which is dedicated to making the world safer through a complete spectrum of security solutions.

 Ludmila Rinaudo | Product Management
Ludmila Rinaudo | Product Management