Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
More About This Author >
Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
More About This Author >
 Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
More About This Author >
Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
More About This Author >
What is Data Security Posture Management (DSPM)?
Data Security Posture Management (DSPM) is an approach to cybersecurity that focuses on protecting the data itself rather than securing the application or infrastructure that houses it.
It achieves this by discovering and classifying data across cloud services and environments, assessing its security posture by identifying vulnerabilities and compliance risks and alerting security teams to initiate remediation efforts.
Imagine a company’s data as a collection of rare artifacts, like ancient manuscripts or priceless jewels. Traditional, infrastructure-focused security focuses on fortifying the building – walls, locks, guards – without knowing the details of its contents.
DSPM, however, is like creating a detailed inventory and proactive protection plan for the artifacts themselves. It’s akin to meticulously cataloging each artifact, noting its type, value, and fragility, and assessing the risk of each artifact being damaged or stolen by considering factors like location and surrounding environment. Based on this information, you implement specific security measures - like climate-controlled display cases or individual alarms.
Why Traditional Data Security Measures Are Failing
Up until relatively recently, traditional infrastructure-focused security strategies were sufficient. Data environments were simpler, data volumes were smaller, and most data resided within on-premises data centers behind well-defined network perimeters. But then cloud adoption exploded, rendering traditional perimeters obsolete, rapidly increasing data volumes, and giving rise to the phenomenon of “shadow data.”
The shift to cloud computing created a complex web of data sprawl, with sensitive data like PII now scattered across diverse cloud platforms, SaaS applications, and hybrid environments. In the cloud, it takes just minutes to spin up infrastructure—often without oversight—creating shadow data and environments that frequently go unnoticed unless deliberately discovered. This, combined with the dynamic nature of cloud access - constantly evolving permissions and user behavior - has further exacerbated risks to cloud data security. To make matters worse, many data privacy regulations now demand granular data control and real-time compliance reporting, which traditional, infrastructure-focused security tools cannot fulfill.
Moreover, the past few years have seen cyber threats grow increasingly fast, frequent, and sophisticated. Traditional reactive cybersecurity measures can no longer keep pace with the most advanced threats, including AI-powered attacks and zero-day exploits. Organizations must turn to proactive measures to protect themselves.
The problem can be summed up as follows: as cloud adoption and data volume have grown and attacks have grown more sophisticated, gaining visibility of and control over data has become more difficult, and proactive security measures have become more important.
The Hidden Risks of Shadow Data
Shadow data can pose a serious risk to organizations. The term refers to data stored in unsanctioned cloud applications, personal devices, and other forgotten repositories. Because this data exists outside of established security frameworks, it is typically unprotected, lacking encryption, access controls, or regular backups. As a result, this data is exposed to unauthorized access, breaches, or accidental loss. Moreover, the lack of visibility hinders compliance efforts – organizations can’t comply if they don’t know where all their data resides.
Why DSPM Matters for Modern Organizations
DSPM is fast emerging as an alternative to outmoded, reactive, infrastructure-focused security measures. It solves many of the most pressing challenges for modern organizations by:
- Addressing Cloud-Induced Data Sprawl: DSPM tools provide organizations with a unified view of their data, regardless of its location. This visibility helps security teams apply consistent security policies and maintain control over data assets in increasingly complex environments.
- Combatting Shadow Data: DSPM tools automatically discover and protect shadow data that often lacks proper security controls.
- Managing Dynamic Cloud Access: DSPM provides granular visibility into user access and enables dynamic policy enforcement, ensuring that access aligns with the principle of least privilege and minimizing the risk of unauthorized data access.
- Meeting Stringent Regulatory Requirements: DSPM tools automate data classification, track data movement, and generate comprehensive audit trials to help organizations meet increasingly stringent data security regulations.
- Proactive Defense Against Advanced Threats: DSPM is a proactive security solution. It continuously monitors data environments to ensure organizations can anticipate and prevent attacks and, hence data breaches, rather than just react to them.
- Protect Data at Rest and in Motion: DSPM is increasingly focused on future-proofing data protection, ensuring data at rest and in motion remains unusable to unauthorized users – even against potential quantum and AI-powered threats.
Ultimately, DSPM tools grant organizations greater control over data - an essential functionality as cloud adoption decentralizes and fragments data environments. They provide a single pane of glass view of data assets and automation tools to remediate security and compliance issues.
Core Components and How DSPM Works
Now that we understand what DSPM is and why it matters, we can explore how it works. Here’s a high-level overview of a DSPM workflow that covers all its foundational capabilities.
Data Discovery
Data discovery, the process of locating and cataloging all data assets, is the first and arguably most important component of DSPM. This component grants security team’s valuable visibility over their data landscape. It involves systematically scanning databases, file systems, and third-party applications across an organization’s entire data environment – including not only traditional on-premises environments but also cloud environments and SaaS applications.
This comprehensive scanning ensures that DSPM tools identify and catalog all data assets, including structured, unstructured, and even shadow data, that security teams may not be aware of.
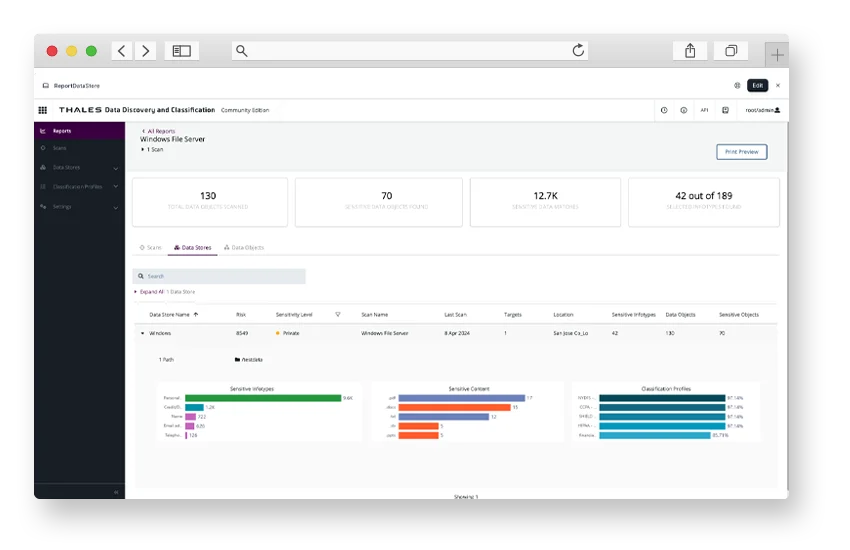
Data Discovery Using CipherTrust DSPM
Data Classification
Once data assets are identified, DSPM tools then classify data based on its sensitivity, potential business impact, permissions, data handling practices, and regulatory requirements. They leverage advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to classify data automatically – a crucial feature for handling the staggering volume of cloud data and accurately identifying sensitive information, even within unstructured data repositories.
Data Protection
Long-established methods like encryption, tokenization, and data masking protect data from unauthorized access or use. Organizations are beginning to build post-quantum-ready environments leveraging advanced versions of these techniques to proactively counter emerging threats powered by AI and prepare for quantum computing.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Armed with a clear understanding of data assets and their sensitivity, DSPM solutions conduct a risk assessment. This process involves identifying potential vulnerabilities - such as misconfigurations, excessive access permissions, data flow and lineage issues, and security policy and regulatory violations – and correlating them with data classifications that delineate sensitivity, breach impact, exploitation likelihood, and compliance obligations. AI/ML-driven contextual insights enhance this process, providing security a deeper understanding of the severity of risks to data and prioritize the possible exposure of the most sensitive data. This correlation helps security teams assign precise risk scores.
Remediation and Prevention
However, DSPM tools aren’t just data visibility tools; they also provide remediation and prevention capabilities. They typically offer guided remediation, providing security teams with step-by-step instructions and recommendations for addressing identified vulnerabilities and policy enforcement capabilities, ensuring that data security policies are consistently applied across the organization’s data landscape.
More advanced tools offer automated remediation, addressing vulnerabilities without the need for manual intervention, and can even integrate with DevOps workflows to prevent application vulnerabilities from making their way into production environments.
Continuous Monitoring
It’s also important to understand that DSPM tools continuously monitor environments for new data assets and risks to existing assets. By doing so, they continuously assess and improve the organization’s security posture and prevent the recurrence of previously identified vulnerabilities.
The Strategic Value of DSPM
How DSPM Streamlines Compliance
In addition to the aforementioned data discovery, classification, and continuous monitoring capabilities, DSPM tools further streamline compliance by automating regulatory workflows. Organizations using DSPM don’t have to rely on manual audits or period checks because these solutions continuously validate data handling practices against evolving standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
DSPM solutions automatically generate audit reports and remediation actions, ensuring that every data asset—wherever it resides—complies with relevant regulations. By monitoring data in real-time, DSPM dramatically reduces audit preparation times and the risk of non-compliance.
How DSPM Enhances Security Operations
DSPM plays a multi-faceted role in security operations, shifting teams from reactive incident response to proactive, data-centric threat management. It offers real-time visibility into an organization’s data landscape, identifying vulnerabilities, shadow data, and misconfigurations that might otherwise go unnoticed, such as identifying data stores that do not meet modern encryption standards. Moreover, as noted, DSPM’s risk assessment capabilities allow security teams to prioritize their remediation efforts, ensuring more effective resource allocation.
How DSPM Bolsters Access Controls
DSPM improves traditional access management by linking data sensitivity directly to user behavior analytics and continuously monitoring access patterns to detect anomalies such as unusual data requests or deviations from normal behavior. This helps organizations enforce the principle of least privilege.
DSPM vs. Other Security Posture Management Tools
You’ve probably heard about some other security posture management tools and are wondering how they differ from data security posture management. While there is some overlap between capabilities, they have distinct focuses that solve different problems. The most often confused solutions are:
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM)
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools focus specifically on the security configuration of cloud infrastructure, such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). They monitor these environments for misconfigurations, compliance violations, and cloud services risks and offer the following capabilities:
- Cloud infrastructure misconfiguration detection.
- Regulatory compliance monitoring for cloud environments.
- Cloud security policy enforcement.
- Visibility into cloud asset configurations.
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM)
SaaS Security Posture Management (SSPM) tools are laser-focused on the security posture of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications, like CRMs or productivity apps. They help organizations manage and secure the settings, configurations, and user access within their SaaS products. Key capabilities include:
- SaaS application configuration monitoring.
- SaaS user access management.
- SaaS security policy enforcement.
- Detection of SaaS-related security risks.
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management
Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management tools address the risks associated with identity and access permissions in cloud environments, managing and controlling who has access to what cloud resources to prevent excessive or unnecessary permissions. They typically provide:
- Visibility into cloud access permissions.
- Detection of excessive or unused permissions.
- Automated remediation of access risks.
- Least privilege enforcement.
AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM)
AI Security Posture Management tools address the unique risks introduced using artificial intelligence and machine learning systems across the enterprise. These tools help organizations monitor and secure AI models, data pipelines, and user interactions to prevent misuse, data leakage, and compliance violations. They typically provide:
- Discovery of AI models and data pipelines.
- Visibility into AI training data and usage patterns.
- Detection of anomalous model behavior and prompt injection risks.
- Controls for access, governance, and responsible AI usage.
DSPM Offers the Foundational Security Coverage
It's important to recognize that DSPM is the foundation for data-centric security, with the broadest scope across the posture management landscape. It inherently encompasses and informs what CSPM, SSPM, and AI-SPM aim to achieve—making it a critical starting point for understanding and mitigating data risk across the entire digital ecosystem. However, the latter tools offer more specialized and in-depth capabilities within their respective domains. These tools are best used in conjunction with one another, but if you can only implement one, implement DSPM.
How DSPM Complements Other Security Technologies
However, it’s not only other security posture management tools DSPM integrated well with; it complements a wide range of security technologies to provide comprehensive protection.
DSPM and IAM for Access Control
DSPM enhances Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools by providing visibility into data stores and, crucially, their permission. IAM defines who can access what, but DSPM reveals what is actually accessible by offering insight into whether those permissions are excessive or misconfigured.
Put simply, DSPM identifies shadow access, overly permissive roles, and data exposure risks that IAM alone cannot. By combining the two, organizations align identity permissions with data classifications to ensure that the least privilege principles are enforced and minimize the attack surface.
DSPM and EDR in Cloud Security
DSPM and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) tools are also complementary. DSPM identifies data stores that could be compromised if an endpoint is breached. Then, if the EDR detects malicious activity, DSPM helps security teams understand the potential impact on data, providing context about data sensitivity and access patterns and enabling more targeted investigations and faster incident response.
DSPM and SIEM
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions aggregate logs and events, while DSPM provides additional data context. DSPM improves the functioning of SIEM tools by feeding them information about data sensitivity, access patterns, and security misconfigurations, which the SIEM tool then correlates with security events to provide a rich context for threat detection and incident response. Ultimately, DSPM’s insights enable SIEMs to prioritize alerts based on data risk and identify patterns that indicate security incidents.
DSPM and DLP for Data Protection
As the name suggests, Data Loss Protection (DLP) tools focus on preventing data exfiltration. DSPM complements DLP in several key areas. First, DSPM identifies sensitive data locations and usage, enabling DLP to enforce policies with real-time accuracy and reducing false positives. Second, DSPM discovers and classifies regulated data, while DLP prevents unauthorized transfers, ensuring compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Finally, DSPM detects vulnerabilities, and DLP blocks data exfiltration, mitigating risks before they escalate.
What to Look for in a DSPM Solution
A DSPM solution is a significant investment, so it is important to make the right choice. When purchasing a DSPM solution, be sure to keep the following considerations in mind.
Operational Factors
- Low Disruption and Simple Deployment: DSPMs should be easy to deploy, integrate with existing systems via APIs, and support various cloud providers and data warehouses – specifically, the ones you use. They should also be asynchronous - requests without waiting for immediate responses – for minimal service disruption.
- Seamless Installation, Rapid Value: The installation process should be straightforward and quick, and the DSPM should deliver results within a short timeframe.
- Intuitive Interface and Strong Technical Support: The DSPM should have a user-friendly interface with clear features, self-support services, and responsive expert technical support.
- Centralized Management: The DSPM should provide centralized control, reporting and detailed views, organized by data governance, privacy, and security functions, enabling a holistic view of the organization's data landscape.
Policy Enforcement Factors
- Integrated Policy Management: The DSPM should provide both pre-built and customizable policies to address a wide range of sensitive data violations and support various asset types and security posture controls.
- Remediation Guidance or Automation: The DSPM should offer guided remediation for policy violations, not just through recommendations, but by enabling direct remediation actions—such as applying encryption, tokenization, or masking. These built-in techniques help enforce best data security and hygiene practices while future-proofing protection against evolving threats.
Data Discovery and Classification Factors
- Autonomous and Cloud-Native Discovery and Classification: DSPMs should leverage cloud provider APIs for automated scanning to detect all data, including shadow data.
- Broad, In-Depth Coverage: Only consider DSPM tools that operate seamlessly across on-premises and multi-cloud environments and support a wide range of data types and formats. Prioritize solutions that can classify all data types—structured, semi-structured, and unstructured—including sensitive assets like encryption keys, secrets, and credentials that are often hidden in less obvious locations.
- Intelligent Classification: Prioritize tools that can accurately identify sensitive data with minimal input.
- Efficient Scanning: Data scanning activities should consider context, avoid redundant scans, and employ sampling techniques to minimize cloud costs.
Analyst Research
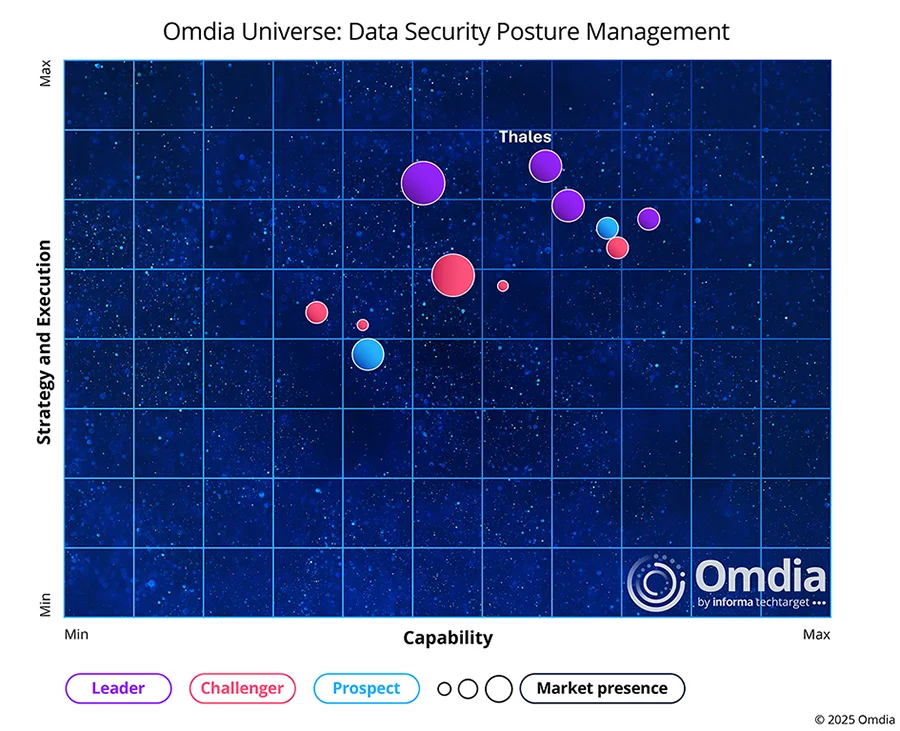
Thales eclipses other DSPMs
See why we’re a leader in the Omdia Universe Report
Best Practices for DSPM Deployment
Stakeholder Alignment and Strategic Planning
As with any deployment, DSPM initiatives begin with the planning stage. Organizations must involve representatives from across the business – including IT, security, data management, and business units – to ensure everyone is on the same page, assign roles, and establish accountability frameworks.
It’s then important to establish clear objectives. Organizations must identify critical assets and understand their significance, evaluate potential threats and vulnerabilities associated with data handling and storage, and ensure objectives align with relevant regulations and industry standards.
Comprehensive Data Discovery and Classification
Once the planning stage is complete, organizations can begin using the DSPM tool to scan and map data, creating a centralized inventory that details data types, locations, and movement patterns. Security teams should classify data based on its sensitivity, availability, and relevance to regulations. It’s also important to document how data is created, shared, and archived.
Continuous Risk Assessment and Prioritization
During the risk assessment stage, assign risk scores based on the predefined classifications. Weigh factors like sensitivity and criticality against how easy it would be for attackers to steal or expose data and assign scores accordingly. These scores will help prioritize remediation efforts—the higher the risk score, the higher priority the vulnerability should be. This is the foundation of effective risk management.
Integration and Automation
As noted, DSPM solutions are best when integrated with other tools. Organizations should assess the compatibility of their DSPM with their existing security tools, configure data feeds, and synchronize access controls to ensure seamless integration. Once integrated, it’s important to conduct thorough testing to ensure everything works as intended.
Granular Policy Enforcement and Access Control
It’s crucial to define access rights based on job functions and responsibilities and regularly audit them. This way, DSPM tools determine whether individuals only have access to the data necessary for their role – the foundation of the principle of least privilege – and alert security teams to any potential issues.
It’s also important to define what data should be subject to what security policies so that DSPM can identify any issues. You should also define automated configuration responses to ensure security teams don’t need to take action themselves.
Continuous Monitoring, Auditing, and Compliance
Ensure the DSPM solution is configured to track user and system behavior, scan for potential threats, and identify potential compliance issues. To maintain compliance, regularly review regulations and, adjust configurations and policies accordingly, and maintain detailed logs of data access and modifications for accountability and forensic analysis.
Scalability and Future Proofing
It’s important to choose DSPM tools that can scale alongside your business, accommodating increasing data volumes and complexity without compromising performance.
Phased Deployment
To ensure smooth implementation, it is important to deploy DSPM with a phased approach, starting with critical data assets and gradually expanding coverage.