 Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager
More About This Author >
Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager
More About This Author >
 Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager
More About This Author >
Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager
More About This Author >
What is passwordless authentication?
Passwordless authentication is an identity verification method that eliminates the need for traditional passwords by using secure, user-friendly alternatives like biometrics (e.g., fingerprint or facial recognition), hardware security keys, and possession-based factors. This minimizes the attack surface, making it exponentially more difficult for malicious actors to gain unauthorized access.
Why are passwords so problematic?
Traditional password-based authentication, once considered a reliable security measure, has become increasingly vulnerable to cyber threats such as brute-force attacks, phishing scams, and credential stuffing.
Passwords highlight a dangerous intersection where outdated technology, flawed processes, and human limitations collide to undermine security. In fact, the Thales Data Threat Report found that 31% of cloud data breaches were the result of human error, and 17% occurred due to a failure to apply multi-factor authentication to privileged accounts.
The Thales Digital Trust Index also found that passwords remain a significant problem for consumers. An overwhelming majority (87%) of consumers said they lost their patience online in the previous 12 months. The top reason cited for that was advertising pop-ups – selected by 38% of respondents – but a close second was password re-sets (31%). Having to re-enter personal information despite having already used the brand was the third leading source for online frustration among consumers.
This frustration can easily translate into a negative impact on brand loyalty. In fact, 17% of consumers surveyed for the Digital Trust Index said they had abandoned a brand in the past 12 months due to forgetting their password. Additionally, 16% cited the need to create long and complex passwords as a reason for switching brands.
Organizations clearly need to prioritize passwordless authentication not just for security, but also consumer satisfaction and brand staying power.
What are the benefits of passwordless MFA adoption?
Aside from being the weakest link in the cybersecurity chain, passwords are incredibly tricky for employees and administrators to manage. Just imagine the costs and productivity gains by eliminating the #1 reason for IT support calls: password resets.
Implementing passwordless authentication can lead to noticeable benefits within months for organizations, including fewer account takeovers, improved efficiency, and fewer headaches for administrative teams. Organizations can reduce costs associated with password resets, help desk support, and credential management.
Passwordless methods also improve the user experience for consumers, partners, and employees by delivering a seamless, frustration-free login experience.
How does passwordless authentication work?
The process typically involves the following steps for a passwordless login.
- A user initiates the authentication process, such as attempting to log in to an application or service.
- Instead of entering a password, the user is prompted to provide an alternative authentication factor.
- The user responds with the requested factor, such as a biometric scan, a one-time code from a mobile app, a passkey or a hardware token.
- The authentication system verifies the provided factor against the user's registered credentials.
- Upon successful verification, the user is granted access to the desired application or service.
What is the role of hardware and software authenticators?
Hardware USB Tokens and smart cards are physical devices that employees can simply plug in to their laptop or tap to their mobile phone to authenticate themselves. Smart cards can combine physical access and digital access making them a reliable choice for high-security working environments.
The new generation of hardware authenticators support the modern FIDO standard (Fast Identity Online) and offers the best defense against phishing attacks and Man in The Middle Attacks.
Software authenticators are convenient solutions that help keep your accounts safe without needing extra devices. That means employees can just use an app on their phone. When they try to log in, the app sends you a notification that you just tap to approve, while temporary or frontline workers use web and pattern-based authentication to access medium sensitive resources.
Types of passwordless authentication methods
Here are a few of the various passwordless authentication methods available:
- Biometrics: Fingerprint scanners, facial recognition, and iris scans offer convenient authentication. Note: it’s important to select biometric systems that mitigate spoofing risks (e.g., advanced liveness detection) and carefully consider privacy implications.
- FIDO Security Keys: These hardware tokens (USB, NFC, Bluetooth) provide robust multifactor authentication. FIDO2 protocols offer strong phishing resistance. Consider vendor options and support for both FIDO U2F and the newer FIDO2/WebAuthn standards.
- Synced Passkeys: This emerging technology leverages platform-based FIDO authenticators, simplifying passwordless access across devices. Passkey’s cryptographic architecture enhances security and user experience.
- Mobile Authentication Apps: Apps like MobilePASS+ generate one-time codes or handle push-based approvals. Ensure the app uses secure communication channels and consider biometric protection for the app itself.
- Certificate-Based Smart Cards and Tokens: Immune to phishing attacks, like FIDO security keys and Passkeys, X.509 certificate-based authenticators provide a high level of assurance when accessing sensitive data hosted in legacy systems not supporting FIDO.
- Pattern-Based Authentication: A convenient authentication solution that overcomes the weakness of passwords without the need for software to be installed or hardware to be provisioned. The end user just needs to remember a pattern on a grid instead of a password or a PIN code.
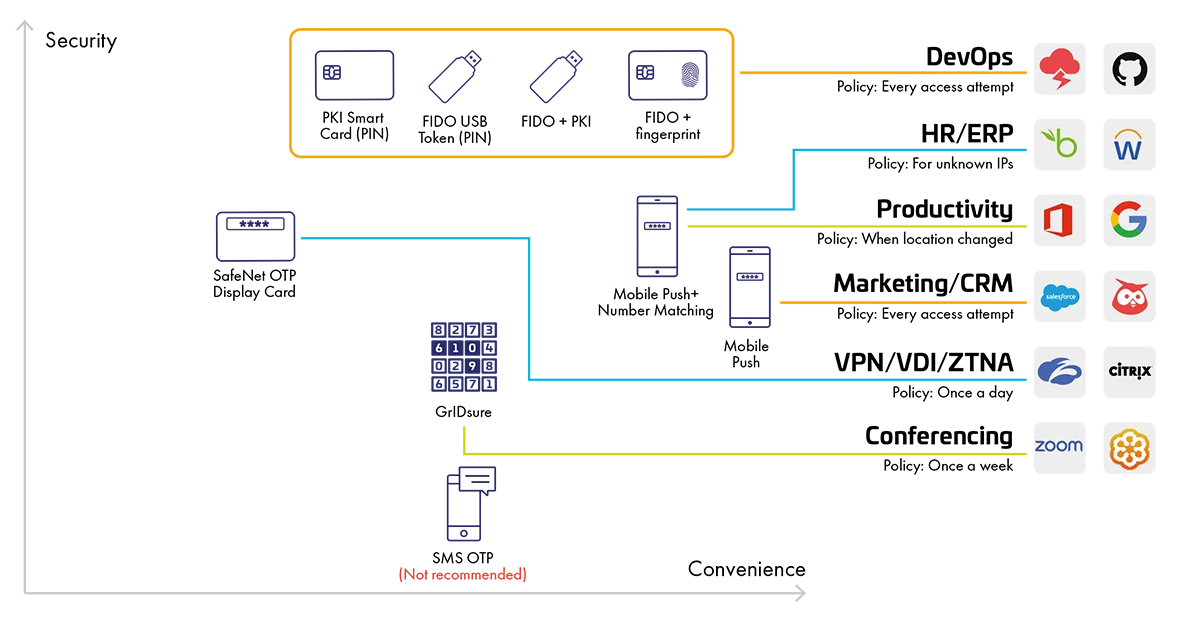
Adopt the Right MFA for Balancing UX and Security
Do you have a favorite passwordless device?
I have many, but if you’re looking for a super convenient and secure way to log in across different devices, I recommend checking out the SafeNet IDPrime FIDO Bio Smart Card. It combines biometrics with NFC, so instead of your employees having to remember a ton of passwords (and bothering IT when they forget), they can simply use their fingerprint to authenticate, and they’re in.
How do passwordless use cases differ, for instance, between a retailer’s workforce and a financial services provider?
There is a difference due to varying priorities and market regulation in each industry. Retailers often prioritize convenience and productivity for their frontline workers, who need quick access to customer data. Lack of productivity and cumbersome authentication mechanisms have a direct impact on retailers’ businesses, so they need to be swift. Financial services, driven by stringent regulations, place a higher priority on security.
However, it’s important to note that passwordless use cases differ primarily due to the sensitivity of the data accessed, the type of users, and the operations being carried out.
While retailers may choose to equip their frontline workers with passwordless authentication methods like mobile or web apps, it’s crucial that they provide privileged users, such as VPs and IT administrators, with strong hardware-based authenticators to protect sensitive data.
How can organizations enforce strong authentication in sensitive environments without relying on mobile devices?
For environments where mobile devices are restricted due to potential interference (Healthcare, Manufacturing) or lack of network connection (critical infrastructures, offshore platforms ...) there are secure passwordless alternatives available:
- On-Screen Pattern or Grid-Based Authentication: This method enables users to authenticate by selecting a unique on-screen pattern. When implemented without additional PINs, this functions as a secure passwordless option.
- Biometric Authentication on Dedicated Devices: If certain devices are permitted, biometric readers—such as fingerprint or iris scanners—can provide strong, passwordless authentication. These devices work well in secure, regulated environments.
- Proximity-Based RFID or NFC Badges: RFID or NFC badges, often used in access control, offer passwordless, hands-free authentication. When integrated with multi-factor protocols, these badges can verify identity securely without requiring passwords.
- FIDO2 USB Security Keys: For environments that allow minimal-use devices, FIDO2-compliant USB security keys or smart cards provide secure passwordless access without risking electromagnetic interference.
These options allow you to maintain strong security without traditional passwords, supporting the passwordless approach even in environments with sensitive equipment restrictions. This enhances both security and user convenience, while reducing risks associated with password management.
What are common challenges to adopting a passwordless strategy?
Addressing a few key challenges along the way can pave a path to a smooth transition to passwordless authentication.
Many organizations depend on older systems and applications that aren’t equipped to support modern passwordless methods. Integrating new authentication technologies with these existing setups can be complicated and expensive, creating a barrier to adoption.
Compatibility can also be an issue, as some passwordless methods may not work smoothly across all devices, platforms, or browsers, which can create usability and access challenges for both employees and customers.
Rolling out passwordless authentication also requires educating users about the new processes. Employees may be hesitant to adopt changes, so thorough training is essential, to succeed the shift to passwordless systems.
Costs are another key factor; the initial investment in hardware, software, and training, along with ongoing expenses, can be a hurdle, especially for organizations with tight budgets.
Despite these challenges, organizations can successfully overcome them and enjoy significant benefits by implementing a sound passwordless strategy:
- Updating legacy systems in stages allows enterprises to gradually adopt passwordless methods without disrupting daily operations, making the transition smoother and more cost-effective.
- Compatibility issues can be managed by selecting flexible, hybrid widely supported authentication solutions that support legacy and modern authentication protocols and work across various devices and platforms.
- To address user resistance, organizations can prioritize user-friendly, intuitive methods, and provide clear, step-by-step training that helps employees and customers understand the benefits of passwordless authentication.
- Note: While advanced MFA methods significantly reduce the risk of credential theft, they do not eliminate the threat of phishing and social engineering attacks. Organizations must educate users on identifying and avoiding these attacks and implement additional security measures.
- While an initial investment is needed, reducing password-related support calls, minimizing security risks, and streamlining user access can provide substantial long-term savings and a stronger security posture.
How can organizations successfully implement passwordless authentication?
This isn’t a straightforward answer because passwordless solutions are not one-size-fits-all. Organizations looking to transition to passwordless should begin by conducting a thorough assessment of their current systems and focus on these essential elements:
- Stakeholder Collaboration: Secure support from executives and involve key teams from the start, including IT, security, UX, and product management. Building a strong business case that highlights ROI and cost factors will help keep the initiative aligned. A dedicated steering committee can maintain focus and alignment across departments.
- Strategic Prioritization: Identify high-impact use cases for passwordless early on, such as systems that handle sensitive data. Begin with pilot programs to address areas where passwordless offers the most security or user experience benefits.
- Authenticator Selection: Select authenticators that best fit your organization’s needs, considering device compatibility, user technical skill, and budget. Evaluate vendors based on security features, ease of use, and overall value.
- Authenticator Life Cycle Management: Plan for the full lifecycle of your authenticators, from setup to retirement, including user support for lost or forgotten devices. Decide whether IT will handle management or if end users will have control, based on your organization’s needs.
At Thales, we’ve created a framework called Passwordless 360° that helps companies make the appropriate next steps toward passwordless authentication. Key steps include user ecosystem mapping, establishing risk-based assurance levels, and completing a gap analysis.
My advice is to start with a pilot program to test the new technology on a limited number of use cases within a small, controlled group, then expand step by step. Engage key stakeholders and provide comprehensive training to ensure a smooth transition.
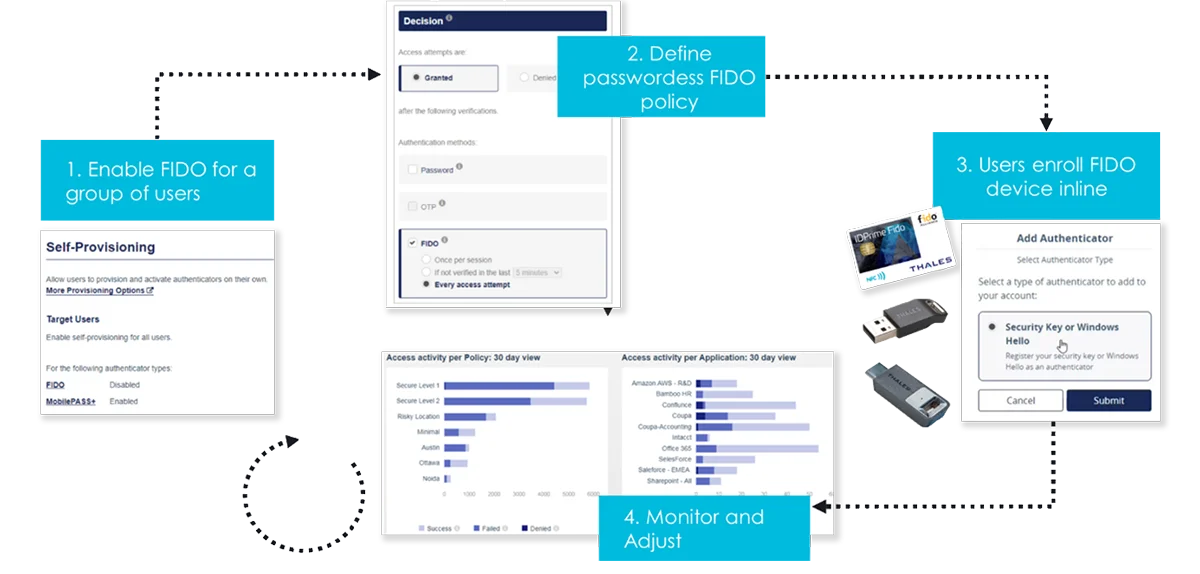
Activating FIDO Authentication with a Passwordless 360° Strategy
How long will passwordless adoption take?
Adoption time can vary, but many organizations see significant progress within a few months. Full deployment is typically achievable within 6-12 months, depending on the organization’s size and complexity. The timeline can be influenced by factors such as the existing IT infrastructure, the scale of integration required, and the readiness of the workforce.
Future trends in passwordless authentication
As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of modern authentication is poised for further advancements and innovations. Here are some emerging trends and predictions shaping the future of modern authentication:
Emerging Trends and Innovations
- Continuous and Risk-Based Authentication: Rather than relying on a single authentication event, continuous and risk-based approaches dynamically assess and adapt authentication requirements based on various risk factors, such as user behavior, location, and device context. This approach provides a more seamless and secure experience while mitigating potential threats.
- Authentication for the Internet of Things (IoT): With the proliferation of connected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), modern solutions will become increasingly important for securing these devices and ensuring seamless user experiences across various platforms and ecosystems.
- Advancements in Biometric Technology: Biometric authentication is expected to continue evolving, with advancements in areas such as behavioral biometrics (e.g., gait analysis, keystroke dynamics), multi-modal biometrics (combining multiple biometric factors), and liveness detection techniques to prevent spoofing attacks.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms will play a crucial role in modern authentication, enabling more accurate and adaptable systems. These technologies can be used for biometric recognition, behavioral analysis, and real-time risk assessment, further enhancing the security and usability of modern solutions.
Predictions and Forecasts
- Adoption Rates and Market Growth: Industry analysts and market research firms predict a significant increase in the adoption of modern authentication solutions across various industries. The global market is expected to experience substantial growth in the coming years, driven by the need for enhanced security and improved user experiences.
- Regulatory and Industry Standards: As these methods gain wider adoption, there will be a need for standardization and regulation to ensure interoperability, security, and privacy. Industry organizations and regulatory bodies are likely to establish guidelines and best practices for the implementation and use of modern solutions.
- The Potential for a Password-Free Future: While the complete elimination of passwords may seem ambitious, many organizations are moving towards this goal, driven by the need for more secure and user-friendly authentication methods.
From biometric verification to mobile-based options, hardware tokens, and advanced cryptographic methods such as passkeys , modern authentication methods offer tailored solutions for diverse organizational needs. Proven effective across industries, these methods enhance security, user experience, and reduce IT costs. As innovations continue, it's crucial for organizations to adopt these solutions, ensuring a secure, password-free future.
The Thales IAM team and I are available to support your passwordless journey. As a next step, I recommend reading about our passwordless adoption framework, Passwordless 360°.
Passwordless 360°
Protecting Your Business, Empowering Your Users
Traditional password-based authentication is fundamentally broken. Consumers, employees, and third-party partners demand a secure and frictionless approach to digital interactions.

IAM Academy is your go-to column for all things IAM, where our experts provide answers to your queries. This is an extended version of an article that originally appeared in our magazine, IAM 360. It focuses on a significant shift in workforce management: passwordless authentication. Sarah Lefavrais, who leads multiple passwordless initiatives at Thales, shares insights on transitioning to a password-free digital environment for employees, consumers and partners.