Incorporating multi-factor authentication (MFA) as a fundamental security measure for your organization is now considered standard practice. It's a sensible decision to utilize MFA. The bigger question is, what type of MFA is best for your organization? The recent social engineering MFA bombing attacks (or push bombing as defined by CISA, the US Cyber Infrastructure Security Agency) have raised concerns about which MFA method businesses should select. FIDO and PKI Certificate-Based Authentication (PKI CBA) have emerged as the go-to options for taking a phishing-resistant approach to MFA; various directives and regulations mandate their use 1.
However, these requirements raise further concerns, especially for organizations that must maintain and protect legacy systems supporting only PKI CBA and modern apps supporting FIDO. How can we combine the best of two worlds in a single phishing-resistant MFA solution?
From MFA to Phishing-Resistant MFA
The MFA bombing attacks, like the ones against Reddit or Uber, do not mean that MFA is ineffective. Any MFA is much better than no MFA, as a recent advisory from CISA highlighted. MFA bombing or MFA fatigue attacks demonstrate the limitations of simple two-factor or multi-factor authentication. In these attack scenarios, the attackers send out repeated targeted phishing attacks to employees until someone gets tired of the notifications and gives up their credentials and the one-time password token.
These attacks also mean businesses should be cautious about their choice of MFA method. Some MFA implementations present proven technical flaws (such as the SS7 protocol vulnerability for SMS). In contrast, others are susceptible to phishing attacks and human mistakes (such as SIM swapping and push bombing).
To ensure the utmost security, MFA should implement secure methods like cryptographic keys, biometrics, and device-level security checks that phishing attempts cannot compromise. Furthermore, passwordless authentication and a zero-trust approach to authentication and security are a MUST.
These considerations led OMB, CISA, and ENISA to require the implementation of phishing-resistant MFA. The OMB mandate also has a deadline – all federal agencies should implement phishing-resistant MFA by the end of the fiscal year 2024.
1 US Executive Order 14028 on improving Nation’s cybersecurity, Boosting your Organisation’s cyber Resilience (European Union), Recommended best practices for administrator in IAM, CISA & NSA.

A Quick Overview of FIDO and PKI CBA
As cyber threats evolve, businesses must adopt robust authentication methods that go beyond traditional passwords to effectively guide against phishing attacks. Phishing-resistant MFA relies on public key cryptography, eliminating the need for shared codes and significantly reducing the possibility of attackers intercepting and replaying access codes. Additionally, phishing-resistant technologies can verify the source and destination's authenticity, ensuring that the authentication process can only occur between the intended site and the user's device.
The FIDO standard, developed by FIDO Alliance and based on the WebAuthn protocol, enables users and organizations to authenticate themselves to online services through FIDO2 security keys, which provide an unphishable standards-based passwordless authentication method. FIDO allows users and organizations to access their resources without a username or password using an external security key. FIDO is a standard that simplifies and secures the sign-in process. It’s especially suited for modern cloud environments and new applications, helping reduce reliance on traditional passwords by using biometric or hardware-based factors.
Certificate-Based Authentication (CBA) works by granting an application the ability to validate and verify the identity of a user based on proof of identity through trusted digital certificates. Digital certificates function as electronic passwords or files. They identify any entity trying to gain access to a resource using cryptography and public key infrastructure (PKI). Most banking applications use CBA behind the scenes and further protect the digital certificate using a fingerprint or a passcode. PKI CBA Is often favored in regulated industries and legacy systems where compliance and trusted identity verification are critical. It supports a broad set of security functions beyond authentication, such as digital signatures and encrypted communication.
Together, FIDO and PKI CBA offer complementary solutions for phishing-resistant MFA: FIDO provides a future-proof and user-friendly passwordless experience for cloud-first scenarios, while PKI CBA delivers a mature and trusted infrastructure for environments with stringent regulatory or legacy requirements.
How Can Businesses Meet This Compliance Requirement?
Businesses can follow the recommendations made by CISA to deploy phishing-resistant MFA .
1. Determine the priority use cases for implementing phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication.
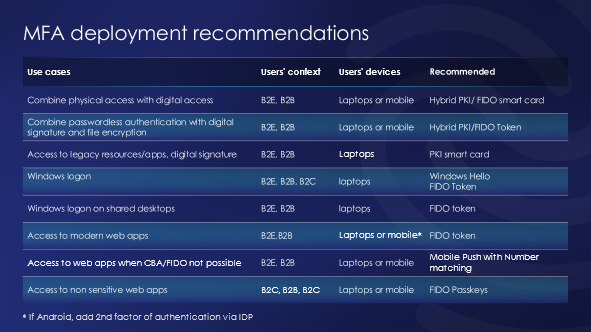
Decisions should be based on the level of risks for users and IT resources to be targeted by cyberattacks. CISA strongly urges system administrators and other high-value targeted users (attorneys, HR Staff, top management, etc.) within the business to implement or plan their migration to phishing-resistant MFA. Highly targeted resources such as email systems, file servers, and remote access systems must be protected with phishing-resistant authentication as a priority.
On the other hand, IT leaders must identify all the systems that may not support phishing-resistant authentication to find alternatives. For example, small- and medium-sized companies that cannot immediately implement phishing-resistant MFA should prioritize enhancing their mobile One-Time Passcodes (OTP) with security features such as number matching, to limit the potential of successful MFA bombing phishing attacks.
2. Examine your IT infrastructure and users’ authentication journeys.
Having clear visibility into your infrastructure and ecosystem – Operational Technology (OT) and IT systems, apps, endpoints, etc. – will allow you to determine where to implement FIDO and PKI CBA authentication. It is essential to remember that legacy systems and apps will require PKI CBA, while modern apps are compatible with FIDO.
In addition, you should map where your employees, partners, and suppliers authenticate from.
- Are they working on shared devices? Are they working in air-gapped areas ? In such context roaming hardware authenticators are more adapted than “platform” authenticators embedded into laptops or mobile devices.
- Do they use mobile devices or laptops? Mobile devices have USB-C connectors, and laptops support both USB-A and USB-C. This is important to decide which form factor you need.
3. Examine your business needs, now and in the future.
- Does your business have any plans to move away from legacy systems and PKI CBA authentication?
- Does your business need to maintain a PKI infrastructure to support use cases such as qualified digital signature or data encryption?
- Do you intend to move processes and data to the cloud and access them through APIs or cloud-based apps?
- Is there a need to support a hybrid authentication environment – PKI CBA and FIDO?
4. Select the phishing-resistant authenticator that fits your needs.
With so many vendors offering MFA solutions, it is vital to examine their offerings.
- Are their authenticators certified by regulation bodies required by your market? For FIDO it is important to look at authenticators certified by the FIDO Alliance
- For PKI, many businesses in regulated markets or technology vendors must comply with international security standards such as Common Criteria, eIDAS or FIPS. Deploying phishing-resistant authenticators certified by regulation bodies such as NIST or ANSSI is a MUST and simplifies your compliance to these standards.
- Opting for an authenticator that either supports FIDO or PKI/CBA option means you will deal with tool sprawl and increased complexity for your end users and IT team. Some vendors offer fused tokens supporting both FIDO and PKI CBA, which brings the advantage to support important additional use cases such as qualified digital signature, data encryption for security , legal & compliance purpose. A single authenticator can be optimal if you operate a hybrid environment.
It is essential to adapt the authentication method to the constraint of your IT resources, to the user's context and find the right balance between security and user experience.
Conclusion
The goal is to achieve zero-trust authentication, verify identities beyond doubt, avoid friction, and protect your organization’s most precious assets - your data and critical systems. Phishing-resistant multi-factor authentication is the way to ensure meeting compliance requirements and building trust with business stakeholders.
Learn more about our security keys and download the infographic “Top 5 Reasons for Choosing SafeNet eToken Fusion Series.”

 Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager
Sarah Lefavrais | IAM Product Marketing Manager