 Haider Iqbal | Director of Product Marketing
More About This Author >
Haider Iqbal | Director of Product Marketing
More About This Author >
 Haider Iqbal | Director of Product Marketing
More About This Author >
Haider Iqbal | Director of Product Marketing
More About This Author >
Over the past year, the world's critical infrastructure (CI) - including energy, healthcare, finance, communications, manufacturing, and transport - has suffered a constant barrage of attacks. The 2024 Thales Data Threat Report, Critical Infrastructure Edition, revealed that almost 93% of CI respondents reported increased attacks. The consequences of breaches in CI can be catastrophic, affecting essential services and even putting lives at risk, which is why securing these environments has never been more crucial.
CI respondents highlighted that Identity and Access Management (IAM) is one of the key technologies to help combat attacks and protect sensitive data. It acts as the backbone of CI cybersecurity by ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information and control systems.
To Err is Human
The report highlighted how the most common root causes of cloud-based data breaches in CI organizations were human error (34%), exploitation of known vulnerabilities (31%), and the failure to use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for privileged user accounts (20%). When analyzing the root causes of attacks by attacker type, misconfiguration (human error) was identified as the top cause for external attackers with financial motivations, geopolitical goals, and other ideological objectives.
Malicious insiders and accidental attacks, often stemming from human error, exploited known vulnerabilities. However, human error can be mitigated, in part, by deploying Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and maintaining audit logs in conjunction with an access management solution.
Among CI respondents, 73% cited MFA as a technology they have chosen to secure access to data in the cloud, which is comparable to the overall global average of 74%.
A Shift Towards External Providers
A noticeable shift is underway in how access control is managed and by whom. Almost half (49%) of those surveyed agree that businesses should maintain control over their access security, compared to 58% in the 2022 survey, indicating a slight shift towards using external providers for access security.
Additionally, 43% believe that access security solutions should be delivered by an agnostic security provider rather than a cloud service provider, and 39% agree that an agnostic access management solution is best for protecting multi-cloud environments.
Regarding zero-trust security, 36% of CI respondents believed that access management and authentication play a key role. The report also said that having more than 50 SaaS applications requires a deeper dive into authentication journeys.
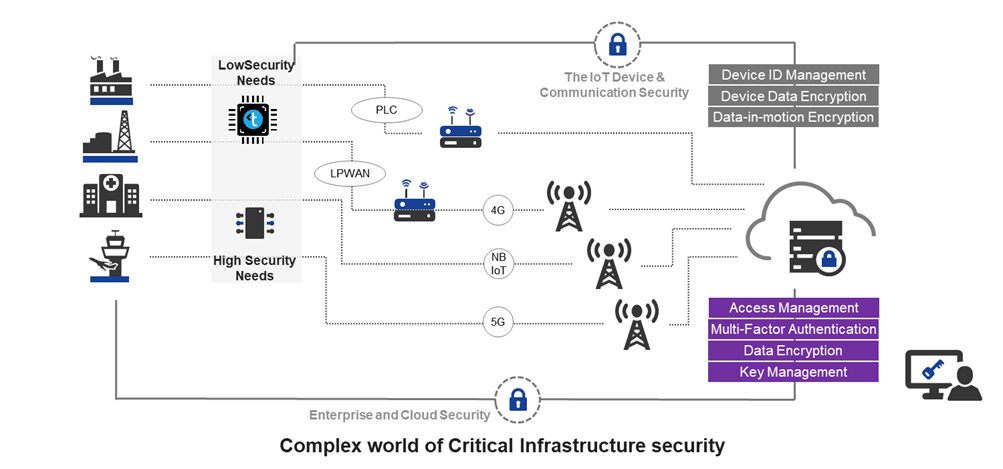
Moreover, because CI entities have a diverse user base, ranging from corporate staff to factory floor workers and field engineers, enabling zero-trust requires flexible access policies. Similarly, an on-premises authentication solution is necessary for air-gapped environments to protect resources.
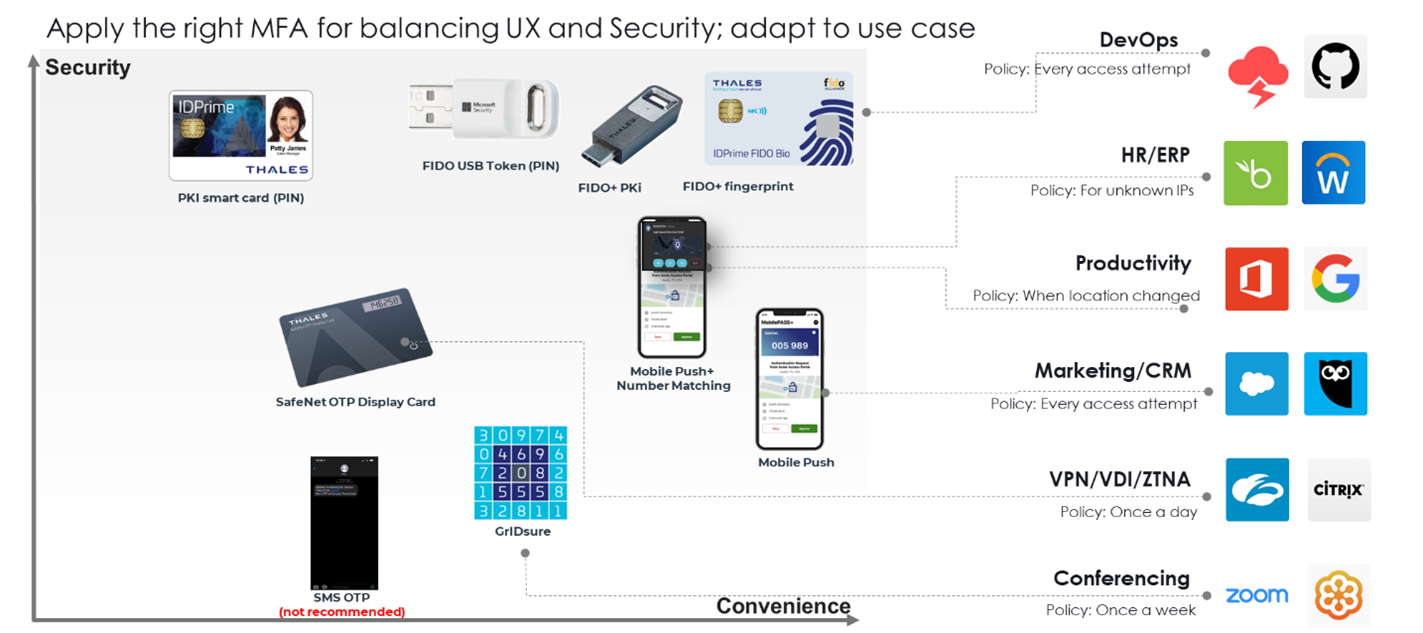
Strong Authentication: Vital for Modern CI
The digitalization of services has revolutionized CI operations, driving enhanced efficiency, remote management, and real-time data insights. However, this transformation also exposes these vital systems to new risks. Alongside remote access becoming the norm, the challenge of securing access to sensitive data and systems has intensified.
Traditional authentication methods, such as passwords, are no longer adequate in protecting against advanced cyber threats. As malicious actors become more adept at bypassing conventional security measures, there is a dire need for more robust, more reliable authentication methods.
Phishing-Resistant Passwordless Authentication
In response to evolving cyber threats, CI entities must transition from traditional credential-based authentication to more secure, phishing-resistant, passwordless approaches. Shared secrets and credentials are inherently vulnerable to phishing attacks. For example, the IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach report indicates that stolen or compromised credentials were the most common initial vector of data breaches. These breaches also took the longest to identify and contain, at nearly 10 months.
To mitigate this risk, organizations should adopt authentication methods that do not rely on such credentials. Passwordless authentication methods, such as device-bound passkeys and FIDO security keys, significantly enhance security by eliminating the human error factor.
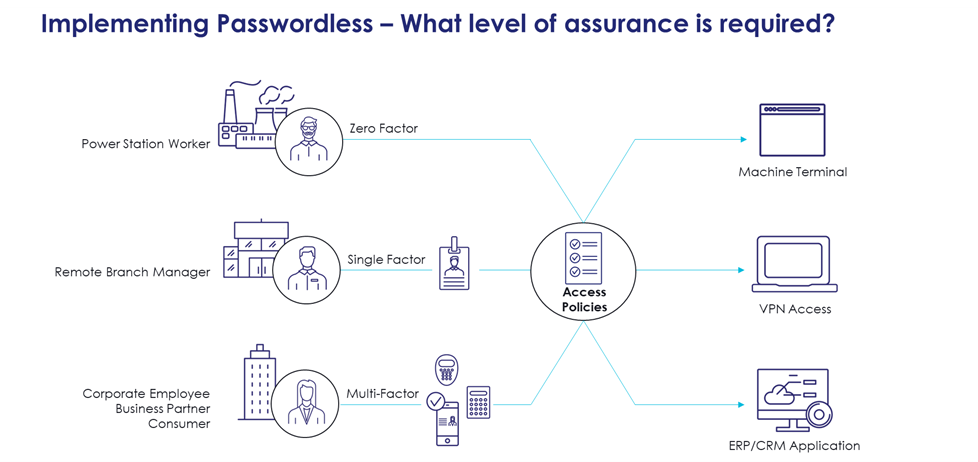
Device-bound passkeys are cryptographic keys stored on a user's device. They provide a secure and user-friendly way to authenticate without passwords. These keys leverage public key cryptography, ensuring malicious actors cannot intercept or tamper with authentication requests.
On the other hand, FIDO keys are hardware-based security devices that support strong, phishing-resistant authentication. They generate a unique cryptographic key pair for each service or application, ensuring that authentication remains secure even if the user's credentials are compromised elsewhere. By incorporating FIDO keys into their IAM strategies, critical infrastructure organizations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and enhance overall security.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Implementing strong, phishing-resistant authentication is a best practice and a necessity for compliance. Regulatory bodies and governments worldwide are increasingly mandating robust cybersecurity measures for critical infrastructure sectors. For instance, the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) recommends adopting robust authentication mechanisms to boost organizational cyber resilience. Similarly, the White House Executive Order 14028 on Improving the Nation's Cybersecurity emphasizes the need for secure authentication methods to protect national critical infrastructure.
Compliance with these regulations helps organizations avoid legal repercussions and ensures the security and resilience of critical infrastructure. By adhering to these standards, organizations can safeguard their operations against cyber threats, protect sensitive data, and maintain public trust.
Prioritizing IAM
The importance of IAM in critical infrastructure cannot be overstated. As the digitalization of services continues to advance, so must the security measures that protect these essential systems. Strong authentication methods provide robust security to defend against modern cyber threats.
By prioritizing IAM and adopting advanced authentication methods, critical infrastructure organizations can secure their operations and safeguard the services vital to our society.
Are you ready to fortify your defenses? Download the full 2024 Thales Data Threat Report—The Critical Infrastructure Edition now to explore the data more deeply and discover how IAM can safeguard your operations against modern cyber threats.