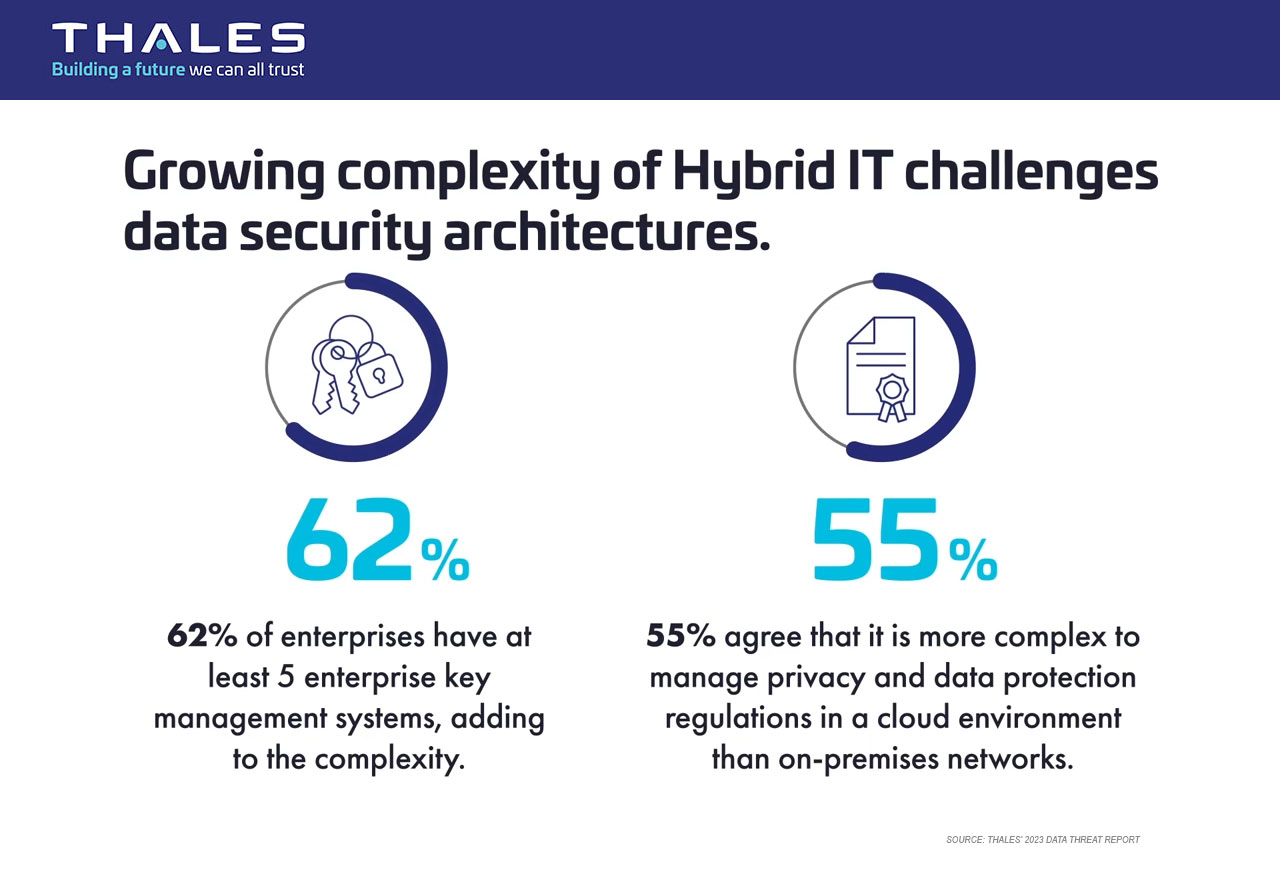
As companies adopt a cloud-first strategy and high-profile breaches hit the headlines, securing sensitive data has become a paramount business concern. The most effective way to ensure data security is through encryption and proper key management.
Key Management as a Service (KMaaS) allows companies to manage encryption keys more effectively through a cloud-based solution instead of running the service on physical, on-premises hardware. In this guide, we will discuss what KMaaS is, how it works, its benefits, and best practices for its implementation.
What is Key Management as a Service?
Key management is a critical aspect of data security and encryption. In the world of cryptography, keys play a vital role in safeguarding sensitive information. These keys are essentially a series of characters or numbers that are used to encrypt and decrypt data, ensuring its confidentiality and integrity. However, managing these keys effectively can be a complex and resource-intensive task for organizations.
Key Management as a Service (KMaaS) is a modern solution that addresses the challenges associated with key management. It is a cloud-based service that enables organizations to securely manage and protect their cryptographic keys. By leveraging the power of the cloud, KMaaS offers a range of benefits such as convenience, flexibility, scalability, and enhanced security, while reducing the burden of key management on IT teams.
In a KMaaS model, a third-party key management service provider takes on the responsibility of managing the cryptographic keys. This alleviates the organization's burden of handling key management internally and allows them to focus on their core business activities. The KMaaS platform provides a centralized dashboard that enables the customer to create, manage, and control cryptographic keys and digital certificates.
The importance and benefits of KMaaS
Using Key Management as a Service is important for data security because it allows organizations to manage their encryption keys consistently in a secure and scalable way. By using a cloud-based KMaaS provider, organizations can centralize and automate their key lifecycle management, reducing the risk of inconsistent policies or compromised keys.
KMaaS providers typically offer features such as FIPS 140-2 certified Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) to ensure the highest security and compliance for sensitive keys.
The benefits of using KMaaS for data security include:
1. Improved key management practices: With KMaaS, organizations can ensure that their keys are managed according to industry best practices, which helps minimize the risk of data breaches.
2. Increased security: KMaaS providers typically have robust security controls in place, which can help to protect against attacks and unauthorized access.
3. Sustained compliance: Encryption and effective key management are key requirements across all security and privacy regulations. With KMaaS you ensure a robust and efficient key lifecycle management to secure encryption.
4. Reduced management overhead: With a cloud-based KMaaS provider, organizations can reduce the burden of managing keys in-house, which frees up resources and allows teams to focus on other security priorities.
KMaaS benefits across an organization
In general, KMaaS can benefit all roles and job functions in an organization by providing a simple and secure way to manage encryption keys across different environments and applications.
- C-suite executives: KMaaS can help C-suite executives to ensure that their organization's sensitive data and assets are secure and compliant with security and privacy regulations. Using a KMaaS solution, executives can have confidence that their encryption keys are being managed properly and that their data is protected from unauthorized access.
- IT security professionals: KMaaS can make the job of IT security professionals easier by providing a centralized platform for managing encryption keys across different environments and applications. KMaaS reduces the complexity of key lifecycle management and ensures that encryption keys are being rotated and managed properly.
- DevOps engineers: KMaaS can benefit developers by providing a simple and secure way to integrate encryption into their applications. KMaaS supports various APIs and developer tools to enable DevOps to add encryption functionality to their applications without building and managing key management infrastructure.
- Compliance officers: A KMaaS solution certified to meet strict regulatory requirements can help compliance officers to ensure that their organization is meeting industry and national regulations on data security and privacy.
With a KMaaS solution, organizations can reduce the key management complexity, improve data security, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
Reduce business threats
Key Management as a Service can help organizations reduce cyber risks and address various threats to business and data security. Managing the encryption keys securely, KMaaS can help protect encryption and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data. Even if an attacker breaches your security controls, KMaaS can help you limit the impact of the data breach by ensuring that the encrypted data remains protected.
With ransomware and extortion being a persistent threat to business economics, KMaaS can help you protect against malware and ransomware attacks by encrypting data at rest and in transit, making it more difficult for attackers to steal or manipulate data.
Besides external threat actors, KMaaS can protect your organization against insider threats by providing granular access controls and ensuring that sensitive data is encrypted and only accessible to authorized personnel.
Compliance is the foundation to effective data security. KMaaS can help organizations comply with industry regulations and standards such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) by providing secure key lifecycle management and encryption services.
How Does KMaaS Work?
In a KMaaS solution, the service provider hosts and manages the key management infrastructure. The customer sends their encryption keys to the service provider, who stores and manages the keys on their behalf. In addition, the service customer can create new cryptographic keys and perform all lifecycle management operations.
The encryption keys are typically stored in Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for added security and never leave the KMaaS platform. Using Thales as an example, each subscription to our key management service, CipherTrust Data Security as a Service, is backed by a Luna Cloud HSM for a FIPS 140-2 Level 3 root of trust.
Through the KMaaS APIs the customer can use the keys to encrypt and decrypt their data across environments and applications as needed.
Throughout the key lifecycle management process, the KMaaS platform typically provides various security features to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the keys, such as access controls, secure storage, backup and auditing.
Components of KMaaS
A typical cloud-based architecture for KMaaS consists of several components working together:
- User Interface: It allows users to access the key management system and perform various operations like key creation, revoking keys, and managing access.
- API Gateway: This component provides a secure interface between the user interface and the key management system. It authenticates the user and ensures all requests are authorized before forwarding them to the key management system.
- Key Management System: This is the core component of KMaaS that manages the keys. It generates and stores keys and performs key rotation, revocation, and other key lifecycle management tasks.
- Cloud Storage: KMaaS relies on secure cloud storage (typically backed by an HSM) to store and manage keys securely. This provides scalability, redundancy, and high availability.
- Authentication and Authorization: This component provides security by verifying the user identity and ensuring that they have the permissions required to perform the requested operations.
- Encryption: Encryption is an important part of KMaaS architecture. Keys are encrypted at rest and in transit to ensure they remain secure.
Overall, the KMaaS architecture allows the platform to be highly scalable, secure, and simple to use. By leveraging the power of the cloud, KMaaS providers offer key lifecycle management services that are highly available, fault-tolerant, and capable of handling the key management needs of even the largest organizations.
Key lifecycle management
In a KMaaS platform, key lifecycle management is typically automated and managed through a centralized system, which can help ensure that keys are properly managed and protected throughout their lifecycle.
KMaaS manage all phases of the cryptographic key lifecycle:
- Generation: A new key is generated for a specific purpose or user using a cryptographically secure random number generator.
- Storage: The newly generated key is securely stored in the KMaaS key repository which is designed to protect keys from unauthorized access, modification, and deletion.
- Retrieval: Based on assigned permissions, the authorized user retrieves the key from the key repository.
- Usage: The authorized user uses the retrieved key to encrypt or decrypt sensitive data, authenticate users or devices, or digitally sign documents.
- Rotation: After a defined cryptographic period or number of uses, the key is retired and replaced with a new one to mitigate the risks associated with key compromise.
- Revocation: If a key is compromised or expired, it is revoked and removed from the key repository.
How KMaaS Helps with Compliance and Sovereignty
As more organizations move their data and applications to the cloud, concerns around data sovereignty have become increasingly important. Organizations must comply with a variety of security and privacy regulations, including GDPR, PCI DSS, and HIPAA, which can complicate the use of cloud-based key management services.
However, key management as a service (KMaaS) providers have evolved to meet the needs of organizations that need to comply with data sovereignty and regulatory requirements.
The role of KMaaS in security compliance
As we’ve already covered, Key Management as a Service (KMaaS) can play a critical role in helping organizations comply with standards and regulations.
Using PCI DSS and HIPAA as examples, both require organizations to implement strong encryption and key management practices to protect sensitive data. KMaaS can help organizations meet these requirements by providing a secure and compliant solution for centrally managing encryption keys.
In particular, KMaaS can provide:
- Centralized Key Management: KMaaS enables organizations to manage encryption keys from a centralized platform to ensure keys are secure and properly managed in accordance with established policies and regulations.
- Automated Key Lifecycle Management: KMaaS automates key generation, rotation, and revocation, ensuring that encryption keys are always up-to-date and secure.
- Secure Key Storage: KMaaS provides secure storage for encryption keys, protecting them from unauthorized access and providing backup and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Compliance Reporting: KMaaS features reporting and auditing capabilities, enabling organizations to prove compliance with industry regulations.
By incorporating KMaaS into their security strategy, organizations can better manage their encryption keys, reduce the risk of data breaches and non-compliance, and more easily meet the requirements of industry regulations.
However, it's important to carefully evaluate your organization's specific business and compliance needs and select a KMaaS provider that can best meet those requirements.
KMaaS and data sovereignty requirements
While you always need to validate, typically companies can leverage Key Management as a Service (KMaaS) and still comply with data sovereignty requirements.
Data sovereignty refers to the legal requirement that data be stored and processed in compliance with the regional or national laws and regulations. Some countries require data localization, where certain types of data, such as personal or sensitive data, be stored within the country's borders.
To help organizations comply with data sovereignty requirements and leverage the benefits of a centralized key management platform, KMaaS providers have designed their solutions to be compliant with these privacy requirements. For example, some KMaaS providers offer the ability to store encryption keys in specific geographic regions.
As previously mentioned, many KMaaS providers offer compliance with industry standards, which include well-defined data sovereignty requirements.
When selecting a KMaaS provider, it is important to ensure that they comply with the specific data sovereignty requirements of the country in which the data is located.
This can be achieved by working with the provider to understand their key management processes and how they address data sovereignty requirements, as well as conducting due diligence on the provider's security practices and compliance with industry regulations.
Myths and Mistakes to Avoid
As with any cybersecurity solution, you may encounter some common misconceptions while researching KMaaS. Here are a few.
"Using a KMaaS solution means I'm giving up control of my encryption keys."
This is a myth. While KMaaS providers are responsible for managing the infrastructure and processes associated with key management, the customer retains control over their encryption keys and can manage them using the KMaaS provider's platform.
"KMaaS solutions are not as secure as on-premises key management solutions."
This is also a myth. KMaaS solutions can be just as secure as on-premises key management solutions and, in some cases, maybe more secure due to advanced security features and techniques.
"KMaaS solutions are only for large organizations."
KMaaS solutions can be beneficial for organizations of all sizes. They can help small and medium-sized businesses implement robust key management practices that might otherwise be difficult to achieve.
"KMaaS solutions are too expensive."
While there is some cost associated with using a KMaaS solution, it is quite competitive to implementing and maintaining an on-premises key management solution. Additionally, the scalability and flexibility of KMaaS solutions can provide cost savings over time.
"KMaaS solutions are not compatible with all cloud environments."
While this may have been true in the past, many KMaaS solutions are now designed to work with a wide range of cloud environments, including those offered by major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Mistakes to avoid
Now that we busted KMaaS myths, let’s look at the other M-word: mistakes.
Implementing a new Key Management as a Service (KMaaS) solution can be a complex process, and there are several typical mistakes that organizations should avoid. Here are a few examples:
1. Not thoroughly evaluating vendors: It's important for organizations to thoroughly evaluate KMaaS vendors before selecting a solution. This includes assessing the vendor's security and compliance capabilities, as well as evaluating the vendor's financial stability and reputation in the market.
2. Failing to plan for integration: Organizations should ensure that their new KMaaS solution integrates smoothly with their existing IT infrastructure. This includes ensuring that the solution is compatible with existing hardware and software, as well as planning for any necessary changes to business processes.
3. Neglecting key management policies and procedures: A KMaaS solution is only effective if it is used in conjunction with well-established and effective key management policies and procedures. Organizations should ensure that they have defined clear policies and procedures for key management and that these are communicated effectively to all relevant stakeholders.
4. Overlooking compliance requirements: Depending on the industry and jurisdiction, there may be specific compliance requirements that organizations must meet when implementing a KMaaS solution. Failure to meet compliance with these requirements can result in legal and financial penalties.
5. Underestimating the importance of training and education: Employees working with the KMaaS solution should be trained to use it effectively and securely. This includes training on key management best practices and any specific features of the KMaaS solution.
Best practices to keep in mind
To wrap things up, KMaaS can play a crucial role in a corporate data security strategy by providing a secure and centralized way to manage cryptographic keys. Encryption is an effective tool for protecting sensitive data, but the keys used for encryption must also be protected. KMaaS provides a way to ensure that these keys are properly stored, managed, and rotated, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or theft.
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when using Key Management as a Service:
- Clearly define your security and compliance requirements: Before selecting a KMaaS provider, identify your security and compliance requirements and ensure the provider can meet them. Consider factors such as encryption strength, key management policies, access controls, and auditing and reporting capabilities.
- Use strong authentication: Ensure that strong authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication are used to control access to the KMaaS platform. This helps to prevent unauthorized access to cryptographic keys and data.
- Regularly rotate your keys: Regularly rotating your encryption keys helps to reduce the risk of compromise and ensures that your data is always protected by strong encryption.
- Back up your keys: Ensure that your cryptographic keys are backed up regularly and stored securely to prevent data loss in case of a disaster or hardware failure.
- Monitor and audit your key usage: Regularly monitor and audit your key usage to ensure that the keys are being used in accordance with your security policies and to detect any unauthorized access or usage.
- Ensure compliance with data protection regulations: Ensure that your use of KMaaS complies with relevant data protection regulations such as GDPR or CCPA. This includes ensuring that appropriate measures are in place to protect personal data and that data subjects are informed of how their data is being used.
- Stay up-to-date with the latest security practices: Stay informed of the latest security practices and technologies and update your security policies and practices accordingly. This includes staying up-to-date with the latest encryption standards, security patches, and threat intelligence.
With a sound KMaaS foundation, organizations can strengthen their corporate security posture and reduce the business risk of data breaches or compliance violations related to encryption and key management. Additionally, KMaaS can help organizations streamline key management processes, freeing up IT resources to focus on other security priorities.
Next Steps
To learn more, we recommend reading Gartner’s report, Select the Right Key Management as a Service to Mitigate Data Security and Privacy Risks in the Cloud.
You can also quickly get started with key management as a service with a free trial of CipherTrust Cloud Key Manager (CCKM), now available as a service on Thales’s Data Protection on Demand marketplace. CCKM provides a central service for controlling encryption keys across multiple clouds – including AWS, Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365, Google Cloud, Google Workspace, Oracle, Salesforce, and SAP.
Visit our CipherTrust Cloud Key Management Service page to learn more.
If you would like to discuss key management services, contact our team of cybersecurity experts for help.

 Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing
Krishna Ksheerabdhi | VP, Product Marketing