 Marko Bobinac | Director of Business Development
More About This Author >
Marko Bobinac | Director of Business Development
More About This Author >
 Marko Bobinac | Director of Business Development
More About This Author >
Marko Bobinac | Director of Business Development
More About This Author >
Enhance remote digital signing security with an eIDAS-compliant Qualified Signature Creation Device (QSCD) for digital signatures and seals
As business processes and government services become increasingly digital, remote signing has become a secure and efficient way to confirm the authenticity of digital documents, transactions, and identities through the use of digital signatures. Digital signatures have become equivalent to traditional handwritten signatures or stamped seals and are legally valid in many jurisdictions around the globe.
As the adoption and legal recognition of digital signatures expands, particularly with evolving regulations like eIDAS and with the use of electronic IDs (eIDs) in Europe which is becoming more common, it is crucial to ensure their authenticity, integrity, and non-repudiation. This involves safeguarding the entire signing process, from guaranteeing signer’s sole control of the signing keys, to incorporated measures against cyber threats, such as data breaches and unauthorized access. In a nutshell, the digital signatures must comply with the stringent legal requirements.
What is Remote Signing?
Remote signing is a method of signing documents electronically, where the signing party utilizes a remote server or third-party trusted service provider to sign digital assets such as documents and files. This allows users to create a digital signature without needing to be physically present at the location where the document or file is processed and stored. Another key component of the digital signing process is remote signature activation, which is done via a Signature Activation Module (SAM) and involves generating or activating a digital signature using a cryptographic key that then needs to be securely managed or stored in a remote location. This enables the signing party to create digital signatures without physically holding the private key needed for signing.
In remote signing, the private key for creating a digital signature is held by a remote server or trusted service provider. The signing party, whether an individual or organization, authorizes specific credentials that allow designated entities to remotely use the private key, ensuring that only authorized users can execute digital transactions on their behalf. While this process enhances trust in remote operations, stringent compliance and audit requirements require additional security measures to protect signature authorization, identity authentication, and private keys.
HSMs can help address these security challenges by providing strict access control mechanisms to the use of signing keys (which must be present inside the HSM to perform the signature), generating secure audit logs and ensuring that keys and signing material are protected within a secure hardware cryptographic boundary.
SAMs also play a significant role in enhancing security for the remote signature process. Since an authorized signer can initiate the signature operation from various devices and through different authentication protocols, additional security controls need to be implemented to ensure end-to-end security. A SAM performs the necessary verifications before the execution of a signature on an HSM, which ensures that the proof of consent of the signature operation is valid and prevents unauthorized use of signing keys. SAMs help protect the integrity and authenticity of the signature process and reinforce trust in remote electronic transactions.
eIDAS Compliant Qualified Remote Digital Signatures:
eIDAS 2 (EU Regulation 2024/1183), introduced in May 2024, builds on the existing eIDAS framework (EU Regulation 910/2014) and includes a phased implementation for EU Member States. eIDAS 2 aims to increase the use of secure remote signing by enhancing the requirements for implementation of Remote Qualified Electronic Signature Creation Devices (RQSCDs), ensuring users retain sole control over their signing keys (even though the signing process happens remotely) and includes a Signature Activation Module (SAM). The SAM is essential for operating remote signing services securely and integrating with digital identity solutions such as the European Digital Identity Wallet (EUDI Wallet). eIDAS is not merely a directive; it’s a regulation, so it’s not open to interpretation and represents European Union law.
To set up a valid eIDAS compliant signing service for creation of qualified electronic signatures, a Trust Service Provider (TSP) must be granted qualified status (QTSP). For this reason, according to eIDAS 2, QTSPs that provide remote QES are defined as a special type of QTSPs that manages remote QSCDs which is certified against Common Criteria (CC). The two main components of a remote QSCD are responsible for:
- Authorization of the signature operation: ensuring that the signer has sole control of their signing keys. This is carried out by a Signature Activation Module (SAM) which activates the signing key within a Cryptographic Module (an HSM). (PP) EN 419-241-2.
- Protecting the key: qualified signatures and certificates require the use of an HSM to protect the keying material. (PP) EN 419 221-5.
eIDAS is widely regarded as the global gold standard for qualified electronic signatures. It establishes the most rigorous legal and technical criteria, making it the reference framework not only within the EU but also for many jurisdictions around the world seeking high-assurance digital identity and trust services.
The influence of eIDAS extends well beyond the EU. Examples include the UK’s post-Brexit UK eIDAS framework, Ukraine’s adoption of Trusted Lists and eID practices, Switzerland’s ZertES law aligned with qualified signature standards, Japan’s My Number Card system reflecting eIDAS-level assurance, Canada’s DIACC referencing eIDAS principles, and eIDAS-inspired cross-border identity initiatives in Australia and New Zealand.
Thales Luna HSMs with Signature Activation Modules:
Remote signing applications utilize a Signature Activation Module (SAM) to authorize the signing operation and authenticate the user’s identity, and HSMs to protect the private keys associated with the digital signatures and secure cryptographic operations.
Luna HSMs are integrated with SAMs from industry-leading Thales Technology Partners Ascertia and Nextsense to deliver secure solutions that comply with the remote signing requirements outlined in the eIDAS regulation for Qualified Trust Service Providers (QTSP). This integration provides organizations with flexible deployment and integration options and seamless operation.
Ascertia and Nextsense offer a Full Remote Qualified Signature Suite and a SAM that can:
- function independently with organizations own signing solution
- be integrated into the out-of-the-box Remote Signing Suite (RSS) from Ascertia and Nextsense

External SAM for Luna HSMs: Thales and Ascertia work together to guarantee essential digital trust products and services that deliver complete digital signature solutions. ADSS SAM Appliance is a Common Criteria Certified Remote Qualified Signature Creation Device (RQSCD) that enables TSP to deliver qualified digital signature services for natural persons, legal representatives, timestamps, and eSeals for any document, web form, or transactions. The SAM Appliance can be shipped with an EN419221-5 certified Hardware Security Module (HSM) or used with a suitable external network connected HSM like the Thales Luna Network HSM to authorize the signing or sealing keys securely.
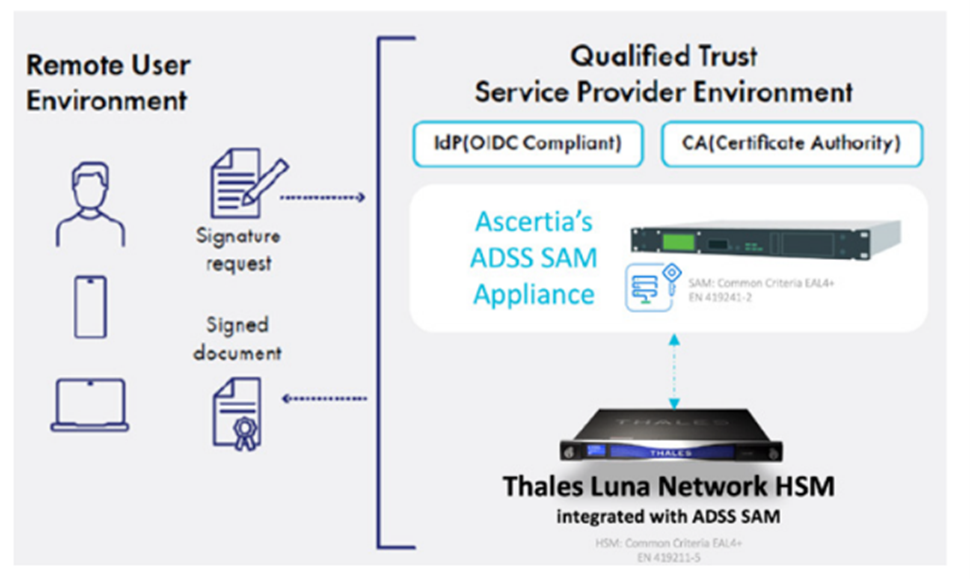
Embedded SAM for Luna HSMs: Nextsense Signature Activation Module (NSSAM), embedded in Luna Network and PCIe HSMs, provides a highly secure, Common Criteria EAL 4+ AVA_VAN.5 certified, EN 419 241-2, EN 419 221-5 and eIDAS compliant solution, scalable and robust for secure remote digital signing and cryptographic operations. The NSSAM ensures that only the authenticated and authorized user activates the process of creating QES under the user’s sole control. These QES cannot be disputed or revoked, supporting legal admissibility. NSSAM together with Luna 7 HSM comprise a QSCD for a signing service that adheres to the remote signing requirements as part of the eIDAS regulation.
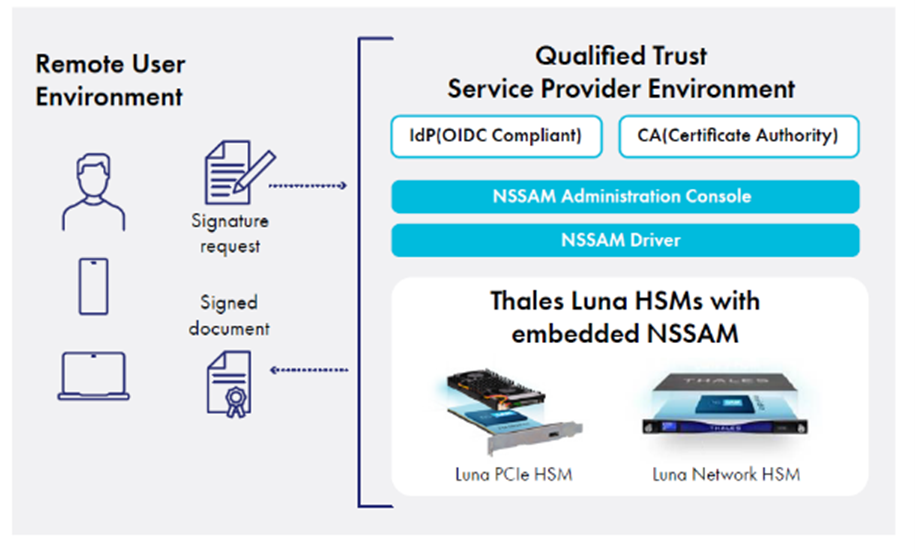
Thales Luna Network and PCIe HSMs: provide the strong performance, high-assurance key protection, and centralized administration/monitoring of crypto operations required for eIDAS compliant electronic signatures, seals and other trust services. Luna HSMs are FIPS 140-3 Level 3 validated, Common Criteria (CC) EAL4+ and eIDAS certified as a Qualified Signature and Qualified Seal Creation Device (QSCD) EN 419 221-5.
Thales Luna HSMs, together with Signature Activation Modules from our Thales Technology partners, are certified under Common Criteria, an internationally recognized security evaluation standard, against a well-defined Protection Profile. This certification ensures a high and consistent level of assurance, supporting global interoperability and fostering trust in highly regulated environments. This trust service is essential, which is why Luna HSMs integrated with SAMs play a vital role in ensuring the compliance, authenticity, and security of digital transactions in today’s increasingly digital world.
Learn more about eIDAS Compliant Qualified Remote Signatures with Luna HSMs.