The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) recently released its annual Threat Landscape Report for 2023. The report identifies the top threats, major trends, threat actors, and attack techniques expected to shape the cybersecurity landscape in the coming years. In this blog, we will summarize the key findings of the report and offer actionable recommendations to mitigate these threats.
Introduction
The ENISA Threat Landscape Report is an annual report that provides a comprehensive overview of the cybersecurity threat landscape. The report is based on a thorough analysis of various sources, including open-source intelligence, expert opinions, and data from multiple organizations. The report aims to provide insights into emerging threats and trends in the cybersecurity landscape and help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture.
Key Findings
As stated, the ENISA 2023 Threat Landscape Report identifies several key threats and trends expected to shape the cybersecurity landscape in the coming years. Some of the key findings of the report are:
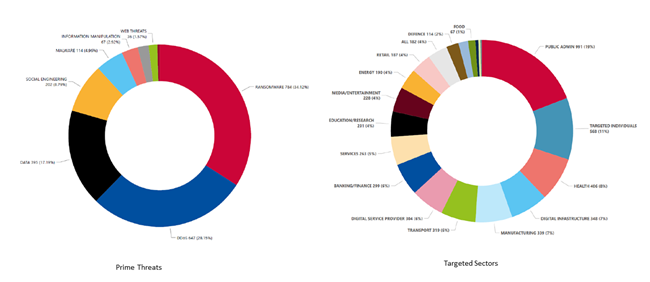
Ransomware still gets top of the podium, accounting for 34% of EU threats. Ransomware attacks are expected to continue to rise in frequency and sophistication. Attackers increasingly use advanced techniques such as double extortion and supply chain attacks to target organizations. The report also highlights that ransomware attacks are becoming more targeted, with attackers focusing on high-value targets with particular emphasis on the Industrial and Manufacturing sectors. Disrupting manufacturing processes or seizing control of industrial systems can result in significant financial losses and operational downtime, making it an attractive target.
The rise of AI-enabled information manipulation is a growing concern for organizations. Attackers exploit the geopolitical environment and use AI-powered tools to create convincing deepfakes, disinformation campaigns, and social engineering attacks. The report notes that these attacks can have significant implications for democratic processes, social cohesion, and national security.
Supply chain attacks are becoming more prevalent and sophisticated, with threat actors misusing legitimate tools primarily to prolong their cyber espionage operations. The extent of the impact of supply chain attacks emerges as a substantial concern in relation to the upcoming EU parliamentary elections. This is because such attacks affected public administration by 21% and digital service providers by 16%.
DDoS attacks continue to be a persistent threat. They are the second most prevalent EU threat. DDoS attacks are getting larger and more complex, are moving towards mobile networks and IoT, and are used to provide support of additional means in the context of a conflict.
Phishing is once again the most common vector for initial access. But the new model, social engineering, is also emerging, an approach that consists of deceiving victims in the physical world.
The report identified public administration as the most targeted sector (19%), followed by targeted individuals, health, digital infrastructure, manufacturing, finance, and transport.
Recommendations
The ENISA report offers a handful of recommendations mapped to ISO 27001 and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. These recommendations can be summarized in the following points.
Ensure your assets are inventoried, managed, and under control. Asset discovery and risk assessment are the foundations of any mitigation plan. A proper data security posture starts with identifying potential targets and conducting a thorough risk assessment.
Perform regular vulnerability scanning to identify and address vulnerabilities. Install security updates and patches regularly, per your patch policy. Establish protocols for vulnerability disclosure and incident notification with external stakeholders.
Ensure remote access technology or other exposed services are configured security, and use phishing-resistant MFA to support strong password policies. Apply the principles of least privilege and separation of duties.
Implement a secure and redundant backup strategy. Ensure you maintain offline, encrypted data backups that are regularly tested, following your backup procedures.
To address new growing risks (in relation to AI for instance), ENISA recommends end-users to protect their data using different techniques including encryption. For this, ENISA refers to “cryptographic controls” defined by ISO27001 (typically cryptographic key management).
Create, maintain, and exercise an incident response plan that is regularly tested. Document the communication flows, both internal and with partners, including response and notification procedures during an incident. A plan B should exist to quickly restore business-critical services and reduce the mean time to recovery. Include key suppliers in business continuity and incident response plans and exercises.
Periodic security awareness training is critical, as social engineering and phishing are the initial actions that open the doors to attacks. Adjust the awareness training to consider the evolving threat landscape and attacking tactics. Consider tailored training focusing on the HR, sales, and finance departments. Also, consider specific training for IT and security staff.
Deploy sufficient security resources to lower the ROI for the attackers. The goal is to make the attacker’s life as hard as possible.
Proper planning and budgeting for data management risks is key and requires alignment in understanding security impacts between management and practitioners.
Zero-trust architectures can increase the security posture of a system by implementing the “never trust, always verify” paradigm.
To operate securely in today’s mobile and cloud-first world, organizations must protect their data and control who has access to it. Thales solutions to discover, protect, and control critical assets enable organizations to modernize data security for a zero-trust world.

 Romain Deslorieux | Director, Strategic Partnerships | Thales
Romain Deslorieux | Director, Strategic Partnerships | Thales