What is Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) and why is it so important to prepare?
Quantum computing is progressing rapidly; it won’t be long before a quantum cyberattack will be possible. Quantum cyberattacks will be able to cripple large networks in a matter of minutes. Everything we rely on today to secure our connections and transactions will be threatened by quantum computers, compromising all keys, certificates and data. Cybercriminals, armed with quantum power to break traditional encryption algorithms, can analyse massive amounts of data or hack critical infrastructure in seconds.
Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC), also known as Quantum-Resistant Cryptography (QRC), focuses on developing cryptographic algorithms and protocols able to stand up to quantum computing power.
Adopt a crypto-agile strategy now, if you haven’t already, and begin to prepare for PQC as soon as possible.
Get started today with our free 5-minute PQC risk assessment tool.
Understanding Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)
Respondents in the Thales Data Threat REPORT said
62%
of respondents in the Thales Data Threat survey said that network decryption was the Post-Quantum Cryptography security threat of greatest concern, with Harvest Now Decrypt Later (HNDL) as the most immediate concern regarding quantum computing
Questions our customers often ask
Quantum computing uses quantum bits known as qubits, which are based on quantum physics that give them different properties than current computers. Quantum computers are not bound to process every combination in sequential order as computers are today. Qubits can process different pieces of information simultaneously producing hundreds of possible solutions all at once.
Today’s public key cryptography is based on factorisation for RSA algorithms, or discrete log problems with DSA, Diffie-Hellman and Elliptic-Curve Cryptography (ECC). Although these are sufficient protection today, using a quantum computer, a hacker would be able to break the algorithms or reduce the strength of the symmetric crypto keys and crypto hashes in minutes. Post-Quantum Cryptography uses a new set of Quantum Resistant Algorithms, created by researchers and tested by industry standard bodies such as NIST and ANSSI that are in the process of becoming a part of compliance requirements.
To begin, quantum computers will co-exist alongside today’s computers, being used mainly for specialised purposes. Initially, quantum computers will not likely supplant cloud servers, but instead work alongside the cloud, providing enterprises and businesses quantum computer capabilities as a service. However, they promise to revolutionise our idea of compute, so it is important to prepare, as much as we can, for future changes in advance by practicing crypto-agility.
To prepare for Post-Quantum Crypto (PQC), evaluate your risk exposure and create a plan to mitigate the risk. A recommended approach is to use hybrid solutions that depend on both classical and quantum-safe algorithms. Start preparing today by assessing your crypto inventory and your overall PQC readiness. Begin planning for a quantum-safe architecture, including support for new algorithms.
First, begin by looking at all your applications that manage sensitive information. If you were to change an algorithm, would the application still work? If not, what do you need to do to make them work? Be sure to do this for every crypto-dependent application in your organisation to map out a plan that will allow for business continuity. Beginning early will help your organisation have a smooth transition to protecting its data in a PQC world.
There are strong indications that the quantum era will begin in the next few years. Organisations generally take a couple of years to implement change throughout their infrastructure. To prepare for a PQC world, organisations need to take steps now to protect their data, intellectual property and more against hackers using quantum computers. For example, often organisations don’t know where their keys are, where encryption is being used or which data is being protected and how. Waiting until quantum computers are generally available is a recipe for years of theft, compromise and a failure to comply with quantum regulations, such as CSNA 2.0 on quantum-safe code signing. With data storage requirements being long-term, hackers are using a Harvest Now, Decrypt Later strategy that creates even more risks in the future.
Certain industries are particularly vulnerable to quantum attacks now and in the future, in part due to the lifespan of the data or keys, but also in part due to the Harvest Now, Decrypt Later strategy being used by cyber criminals. Any software requiring authentication for smart devices in IoT, confidential communications using VPN, digital identities used by governments and enterprises to validate users, as well as any keys or data with a long lifespan such as in Code Signing certifications, Public Key Infrastructure or medical devices.
Preparing your organisation for a quantum future today
Rather than being reserved for science fiction films, quantum computers exist today as organisations drive towards commercialisation.
Post-quantum readiness starts with crypto-agility
Crypto-agility is a business strategy that enables you to future-proof your organisation by:
- Having the flexibility to quickly change protocols, keys and algorithms
- Using flexible, upgradeable technology
- Reacting quickly to cryptographic threats, such as Quantum computing
- Adding to your tech stack with minimal to no disruption
Thales products have been purposely designed to help you be crypto-agile and quantum-safe.
Building a future-proof post-quantum strategy
Securing an enterprise against quantum threats requires cybersecurity solutions that support Quantum Resistant Algorithms (QRA), and also offer options for Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) and Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG). Thales is committed to delivering solutions that support a post-quantum crypto-agile strategy.
Quantum Resistant Algorithms
QRAs are fundamental to protecting against quantum attacks, whether lattice-based, multivariate, hash-based or code-based cryptography
Quantum Key Distribution
QKD distributes encryption keys between shared parties based on the principles of quantum physics and the properties of quantum mechanics
Quantum Random Number Generation
QRNG is a high bit rate random number source harnessing the inherent randomness in quantum mechanics to create encryption keys
There are three component parts of a quantum safe solution, which we’ve done in our work with Wells Fargo to take some risks off the table. It starts at the key generation stage: how do you create the keys that you're using in your system? What type of keys are they? Then there is the algorithms and how do you look after them? That's the management aspect. Finally on the generation front, we are looking to produce keys that are fundamentally unpredictable. These three items are the definition for a strong key.

Kick off post-quantum readiness with the PQC Starter Kit
Thales and Quantinuum have partnered to create a PQC starter kit that accelerates the process of testing quantum-resilient measures in a safe environment.
Thales quantum-ready solutions

Rely on Luna HSMs as the market-leading crypto-agile foundation of digital trust to reduce risk, ensure flexibility, easily manage keys and simplify integrations.
Protect encryption keys with Luna Hardware Security Modules
HSMs protect quantum-safe keys:
- Hash Based Signing (SP 800-208)
- HSS – Hierarchical Signature Scheme (multi-tree version of LMS)
- XMSS – Extended Merkle Signature Scheme
- XMSSMT – XMSS Multi-Tree
- SPHINCS+ (SLH-DSA)
- Kyber (ML-KEM)
- Dilithium (ML-DSA)
Implement your own Post-Quantum Crypto using Luna’s Functionality Module (FM) or with various Partner FMs/integrations
Inject quantum entropy with QRNG and Luna HSM’s secure key storage
Address critical applications where high-quality random numbers are vital
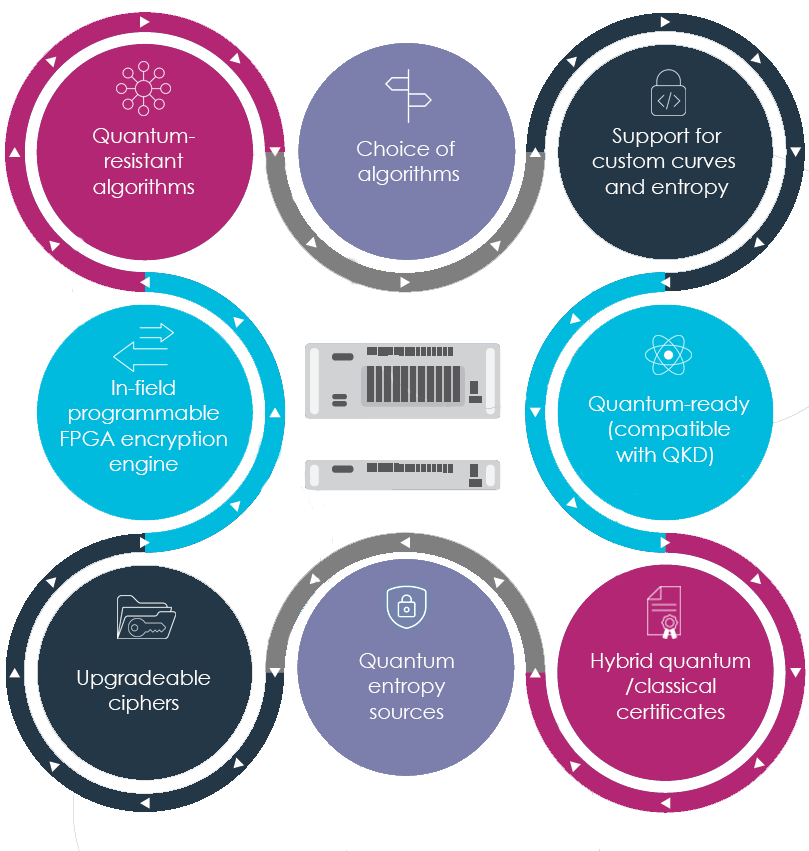
Secure data in transit with High Speed Encryptors (HSE)
Thales HSEs include a framework to support QRA via firmware upgrade. Thales HSE solutions support all four NIST Quantum Resistant Public Key algorithms (finalists) in all products (plus other non-finalist algorithms).
Thales HSEs are quantum-ready and QKD compatible for more than a decade.
Quantum Random Number Generation is integrated into the HSE solution.

Thales HSE network encryption solutions support Post-Quantum Cryptography with a crypto-agile, FPGA-based architecture.




















