Key principles of Zero Trust security models
- Trust no one – verify everywhere
- Adopt a ‘default deny’ stance
- Secure applications at the access point
Zero Trust Security Architectures
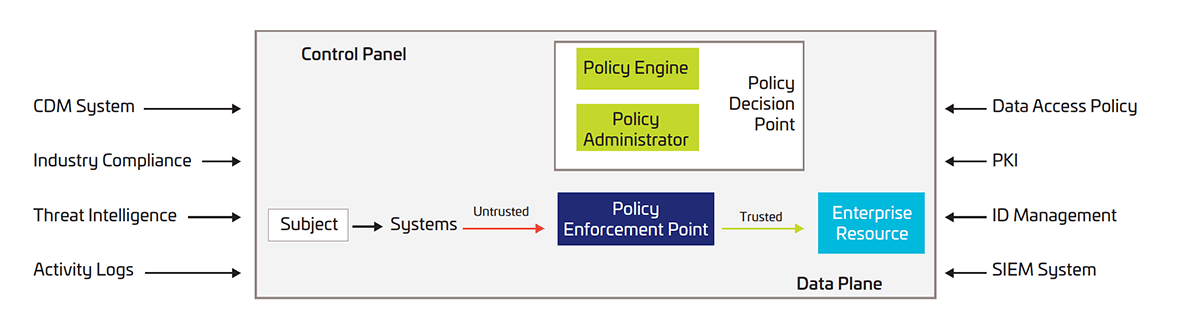
NIST describes three approaches to building an effective Zero Trust security architecture.
Identity-centric
The identity-centric approach of Zero Trust architecture places identity of users, services and devices at the heart of policy creation. Enterprise resource access policies are based on identity and assigned attributes. The primary requirement to access corporate resources is based on the access privileges granted to a given user, service or device. To cater for a more adaptive authentication, the policy enforcement may consider other factors as well, such as device used, asset status and environmental factors.
Network-centric
The network-centric approach of Zero Trust architecture is based on network micro-segmentation of corporate resources protected by a gateway security component. To implement this approach, the enterprise should use infrastructure devices such as intelligent switches (or routers), Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW) or Software Defined Networks (SDN) to act as policy enforcement protecting each resource or group of related resources.
Combination approaches
A cloud-based combined Zero Trust architecture approach leverages cloud-based Access Management and Software at the Service Edge (SASE). The cloud-based Access Management solution protects and enforces the identities of cloud applications and services, while SASE components, such as Software Defined Networks (SDNs) or Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW) protect on-premises resources.







