 Darim Rahmatallah | Senior Product Manager, Thales
More About This Author >
Darim Rahmatallah | Senior Product Manager, Thales
More About This Author >
 Darim Rahmatallah | Senior Product Manager, Thales
More About This Author >
Darim Rahmatallah | Senior Product Manager, Thales
More About This Author >
In this blog, we break down what the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) is, who it applies to, and why it’s so important for any company that wants to sell digital products in Europe. Then, we’ll guide you through the essential cybersecurity requirements outlined in the CRA. You’ll walk away with a clear understanding of the actions to take at each stage of the development cycle to ensure your products are built with compliance in mind from the start and how Thales can help you get there.
What Is the European Cyber Resilience Act (CRA)?
The Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) is a key piece of EU legislation that establishes mandatory cybersecurity standards for digital products. Unlike existing network security directives that focus on infrastructure, the CRA’s requirements focus on securing the software products themselves.
What’s the Goal of the EU’s Cyber Resilience Act?
The purpose of the CRA is to enhance cybersecurity across the EU and keep the average consumer safe.
In the past, there was not enough accountability for cybersecurity when it came to software products sold in Europe. Now, compliance with cybersecurity standards is a prerequisite to selling into the EU market. Products need to be secure by design. Providers must clearly communicate cybersecurity risks to users and have a plan to correct vulnerabilities when discovered.
Who Does the CRA Apply To?
The Cyber Resilience Act applies to anyone who wants to sell a product with digital elements into the EU. This includes manufacturers and developers who create products with digital elements. It also extends to resellers and distributors who sell into the EU.
What Products Need to Be CRA Compliant?
The CRA regulations cover both hardware that contains digital elements and pure software products. The CRA requirements must be met regardless of the connectivity status of your product. That means even if the software you sell never connects to the internet, it must comply with the CRA. On the other hand, the CRA excludes pure Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offerings. So, if you’ve developed an app that is sold completely as a service and does not have any physical element to it, the CRA should not apply to you.
Examples of Products in Scope of the CRA
Hardware with digital components:
- Industrial/manufacturing IoT
- Smart devices
- Storage media
- Network controllers
- Any other physical products with digital functionality
Software:
- Operating systems
- On-premises software and desktop applications
- Remote data processing solutions
- Mobile applications
- Video games
Examples of Products Not in Scope of the CRA
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS):
The CRA is a product law, so pure service offerings are not in scope. - Unfinished software:
Alpha or beta versions don’t need to be CRA compliant. - Non-monetized open-source software:
Open-source software is only covered if it's monetized by manufacturers or developers. - Industries covered by other regulations:
Some sectors, like automotive, medical, and defense, already have mature industry-specific regulations, so they are not in scope.
The CRA is designed to enhance security across the digital landscape that is not currently regulated. An applicability assessment will determine if your specific products require CRA certification.
Compliance Penalties
The implications of non-compliance with the CRA are severe and potentially business threatening. Market surveillance authorities will have the power to enforce penalties, making compliance a business necessity.
Products found to be non-compliant face:
- Sales restrictions across the EU market
- Product warnings that can cause significant negative PR
- Product recalls from the European market
- Financial penalties ranging from €5–15 million or 1–2.5% of worldwide annual turnover
Key Manufacturer and Software Developer Obligations Per Development Stage
If you plan to sell in Europe, your products must comply with the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA). That means it is imperative to make cybersecurity a core part of how you plan, build, distribute, and support your products.
Below is a breakdown of the essential cybersecurity requirements outlined in the CRA, along with the stages at which each requirement must be addressed.
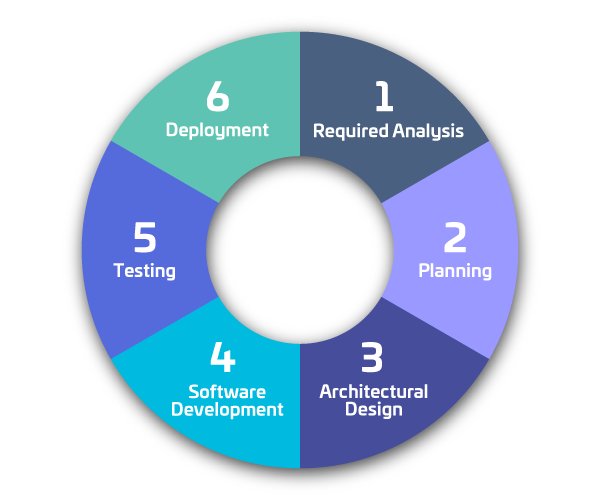
Software Development Lifecycle
Risk-Based Design
Requirement: Implement state-of-the-art security measures and best practices throughout development to address identified risks.
Action: Your design needs to take cybersecurity into account. Integrate best practices and state-of-the-art security tools into development.
Secure Configuration
Requirement: Deliver products with secure default settings and allow users to reset to a secure state if needed.
Action: Ensure default settings are secure and protected from tampering or unauthorized changes.
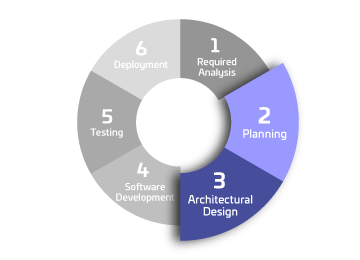
Exploitation Mitigation
Requirement: Eliminate known vulnerabilities and limit attack surfaces to reduce the risk and impact of security incidents.
Action: Report attacks and describe mitigation steps. Reduce attack surfaces through encryption, obfuscation, and secure coding.

Timely Security Updates
Requirement: Address vulnerabilities through automatic or user-notified updates, with an opt-out option where applicable.
Action: Identify at-risk users and provide timely updates. Notify users quickly and clearly.
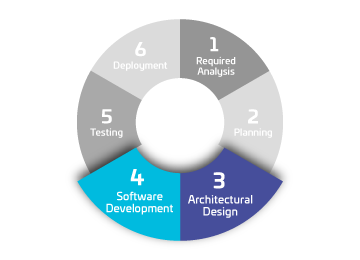
Access Control
Requirement: Prevent unauthorized access using authentication, identity management systems, access logging, and breach reporting.
Action: Use strong authentication and license-based user access control for maximum security.
Data Minimization & Security
Requirement: Process only necessary data, safeguarding confidentiality, integrity, and availability with encryption and secure mechanisms.
Action: Only collect essential data and secure it in transit and at rest.

Integrity & Monitoring
Requirement: Protect data integrity, monitor internal activities, and allow users to opt out of monitoring where appropriate.
Action: Monitor for data theft or tampering. Limit monitoring to system integrity rather than user behavior.
Availability & Resilience
Requirement: Ensure essential functions remain operational after incidents, mitigating risks such as denial-of-service attacks.
Action: Apply secure coding and intrusion prevention. Use encryption and obfuscation.
Data Removal & Portability
Requirement: Provide secure options for data deletion and the ability to transfer data between products or systems.
Action: Enable full data deletion with no ability to recover deleted information.

How Can Thales Help You Be CRA Compliant?
Thales is a global cybersecurity leader, providing both organizations and end users with confidence in the security of the products they use.
Our solutions help you manage security across distributed components and complex technology environments by protecting against hacking, reverse-engineering, intrusions, and malicious attacks. At the same time, all Thales products are designed to keep access simple and seamless for legitimate users. Talk to one of our security experts to learn more.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is accurate as of Summer 2025. At the time of writing, the Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) remains subject to ongoing litigation and potential changes. Readers are advised to consult the latest legal updates or official sources to ensure they have the most current information.
