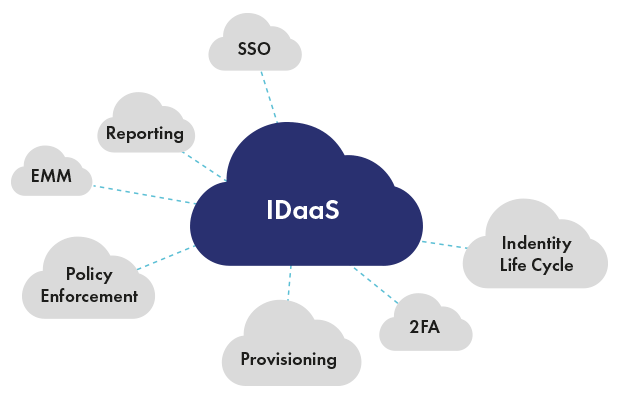
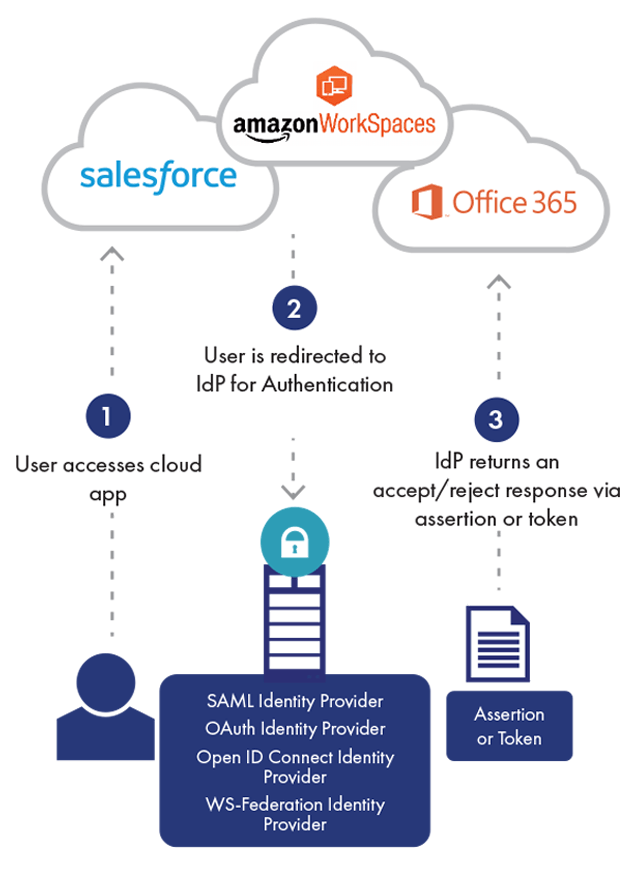
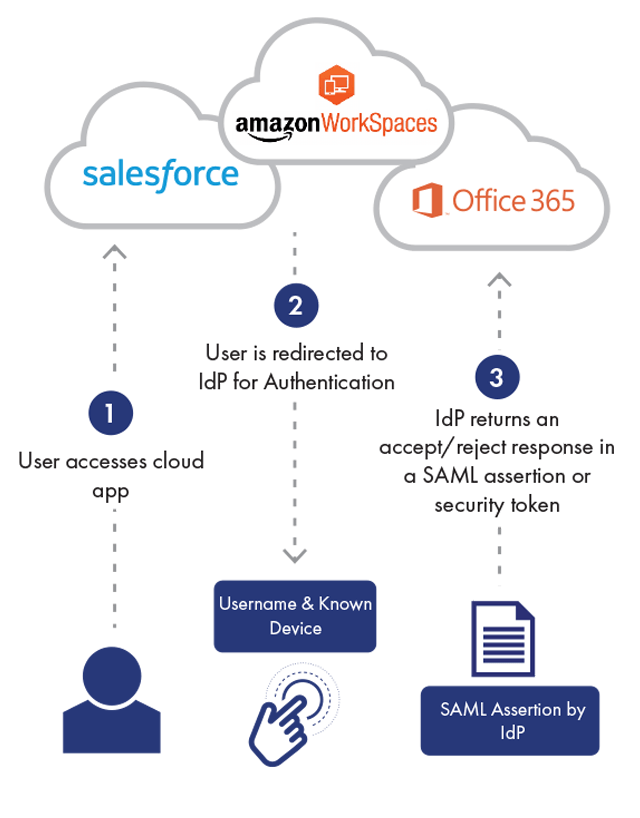
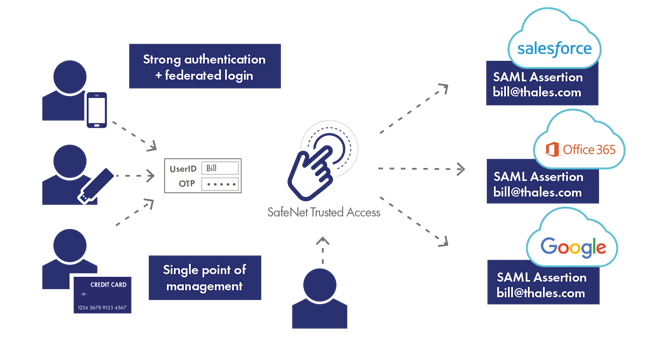
Continuous authentication is a form of authentication that takes place continuously, each time a user accesses a new application or resource, in contrast to one-time or binary authentication, which provides a one-off yes/no decision that is only valid for a single login to a single application.
With a token, a password or a fingerprint – authentication is basically a yes / no decision: The system validates a user’s identity and either allows or denies them access to an application.
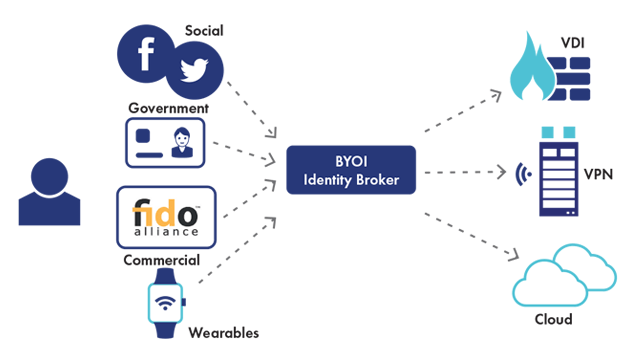
But thanks to newer technologies, such as context-based authentication or behavioral biometrics (for example, browsing pattern, typing pattern and other physical traits), authentication can become a more continuous process. By assessing a range of attributes such as IP address, mobile parameters, known device, operating system etcetera, contextual or risk based authentication can continuously verify a person’s identity each time they log into an application. In fact, it can do so without the user even knowing.
Contextual authentication offers many frictionless ways of verifying a person’s identity. And this is what allows balancing user convenience with the ability to apply granular access controls to numerous cloud applications. And this is why the concept of continuous authentication – which is based on context-based authentication – is a foundation of cloud access management.